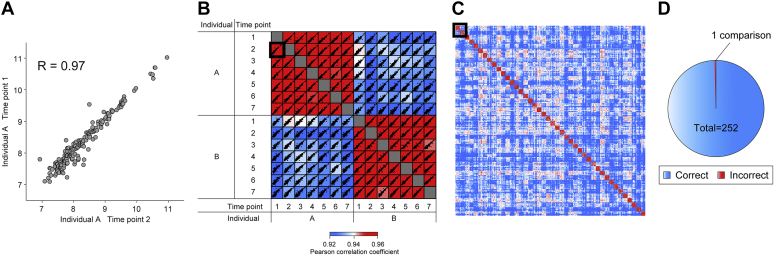
Fig. 1.
Identifying participants in a longitudinal study by correlation of individual-specific proteins.A, correlation of individual-specific proteins of time points 1 and 2 of individual A. B, seven longitudinal samples of two individuals, A and B, are correlated with each other (Pearson correlation coefficient is color-coded, with color bar below). The comparison displayed in (A) is highlighted by a black frame. C, cross-correlated individual-specific proteins of all samples of the weight loss study. The correlation matrix shown in (B) is highlighted by a black frame (Pearson value coded according to the same color bar). D, identification of individuals by correlating individual-specific proteins. Proteomes of the reference time point were compared with all other time points in turn. The percentage of correctly and incorrectly assigned participants is color-coded.