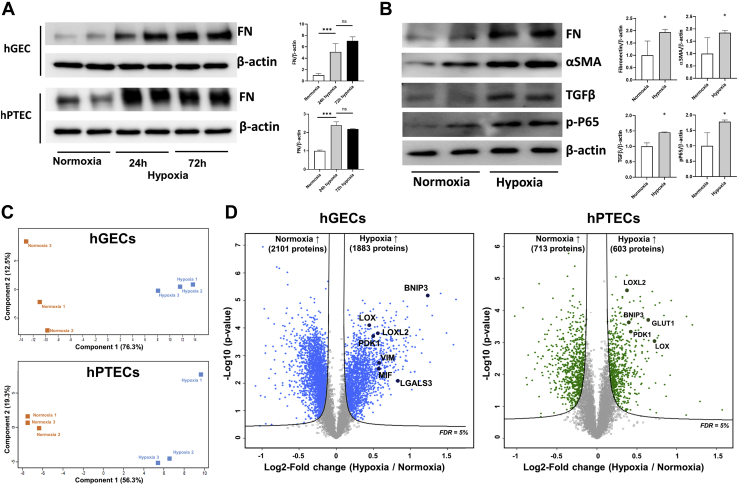
Fig. 4.
Identification of the differentially expressed proteins from the human renal cell lysates under normoxic and hypoxic conditions.A, fibrosis was induced with a 24-h as well as a 72-h hypoxic injury. A representative blot and densitometry analysis of western blot for fibronectin after hypoxic injury is shown. Error bars represent standard deviation. ns, not significant; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. B, for the confirmation of chronic injury following hypoxic damage in human GECs, western blot analysis was performed for fibronectin, α-SMA, TGF-β, and phospho-Ser536-P65. A representative blot of three independent experiments is shown. The densitometric analyses of these blots are shown on the right. Error bars represent standard deviation. ∗p < 0.05. C, principal component analysis plot of the cell-derived proteins from control and hypoxic-injured renal cells using the first two principal components. Upper and lower plots represent principal component analyses for GEC and PTEC, respectively. The plot displays PC1 on the x axis and PC2 on the y axis. D, volcano plot depicting the variance in expression between normoxic and hypoxic human primary cultured renal cells. Left and right plots represent volcano plot for GEC and PTEC, respectively. Marked data points indicate the previously known proteins related to inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis processes. The solid line indicates the cutoff based on false discovery rate <5%.