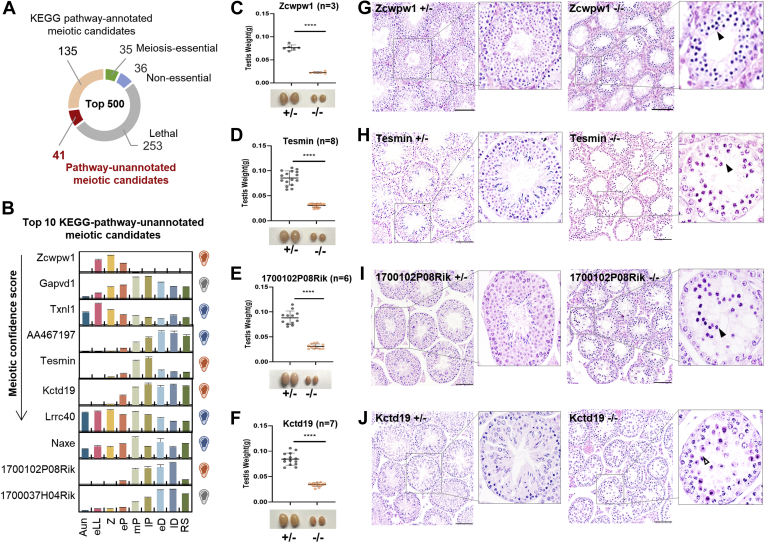
Fig. 7.
Phenotypic validation of the meiotic-essential proteins predicted by the FuncProFinder-RBF.A, distribution of the phenotype annotations and the KEGG pathway annotations in the top 500 meiosis candidates. B, dynamic abundances of the top 10 RBF-ranked meiosis candidates. The error bars represent SEM in triplicates. The bulbs on the figure (right) indicate the validated phenotypes of KO mice, orange as meiosis-essential, blue as meiosis nonessential, and gray as lethal. C–F, comparison of the weights of the testes derived from the 8-week-old Zcwpw1+/− and Zcwpw1−/− mice (C), Tesmin+/− and Tesmin−/− mice (D), 1700102P08Rik+/− and 1700102P08Rik−/− mice (E), and Kctd19+/− and Kctd19−/− mice (F). ∗∗∗∗ represents p < 0.0001 in unpaired two-tailed t test. G–J, cross sections of the H&E-stained seminiferous tubules from the heterozygous and homozygous knockout mice of the aforementioned four genes; the insets denote the specific seminiferous tubules under a higher magnification. The filled arrows point to the pachytene-like cells. The hollow arrows point to the metaphase I-like cells. The scale bar represents 50 μm. KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; RBF, radial basis function; RS, round spermatid.