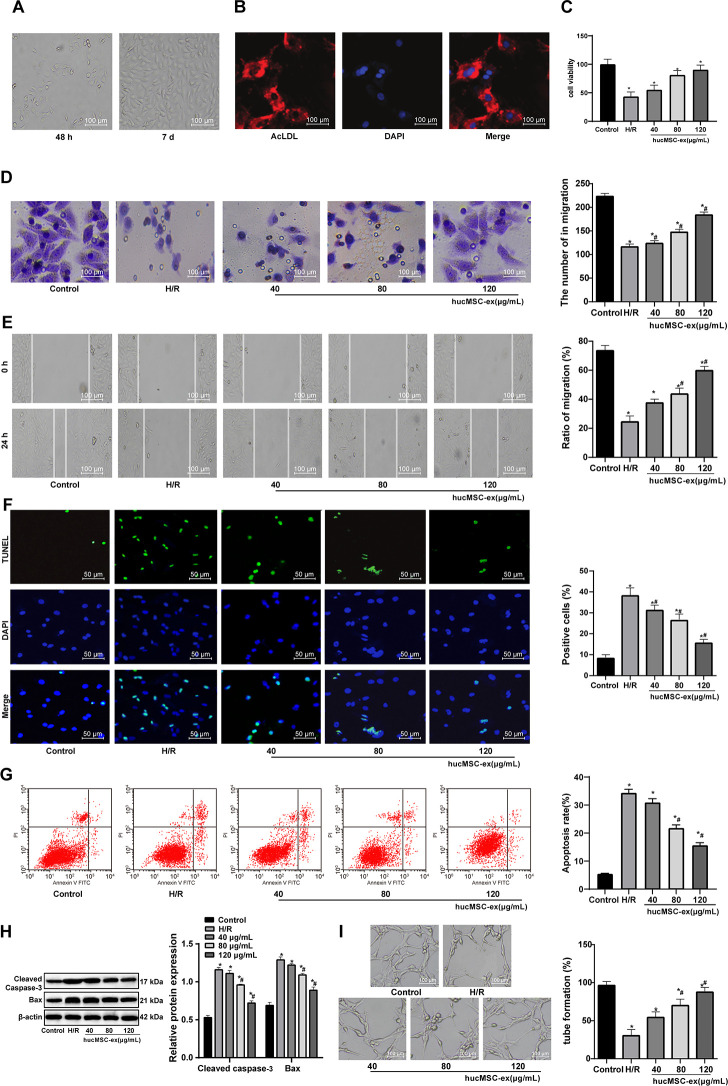
Figure 2.
The hUCMSC-ex facilitates growth and restrains apoptosis of H/R-damaged CMECs in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) CMECs observed under microscope after 48 h (left) and at the 5-7th d (right) of cell culture. (B) Dil-ac-LDL-positive CMECs (red) and DAPI-positive (blue) under fluorescence microscope after 7 d of cell culture. (C) Viability of CMECs detected by CCK-8 after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex. (D) Invasion of CMECs assessed by Transwell assay after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex. (E) Migration of CMECs evaluated by scratch test after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex. (F) The number of TUNEL-positive CMECs after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex. (G) Apoptotic rate of CMECs assessed by flow cytometry after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex. (H) Expression of apoptosis-related proteins Cleaved caspase3 and Bax in CMECs after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex measured by Western blot assay. (I) Tube formation in CMECs after co-culture with hUCMSC-ex. *p < 0.05, vs. the control group; #p < 0.05 vs. the H/R group. All experiments were repeated 3 times. Data in panels (C–G, I) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and data in panel (H) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, and the pairwise comparisons after ANOVA were performed with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.