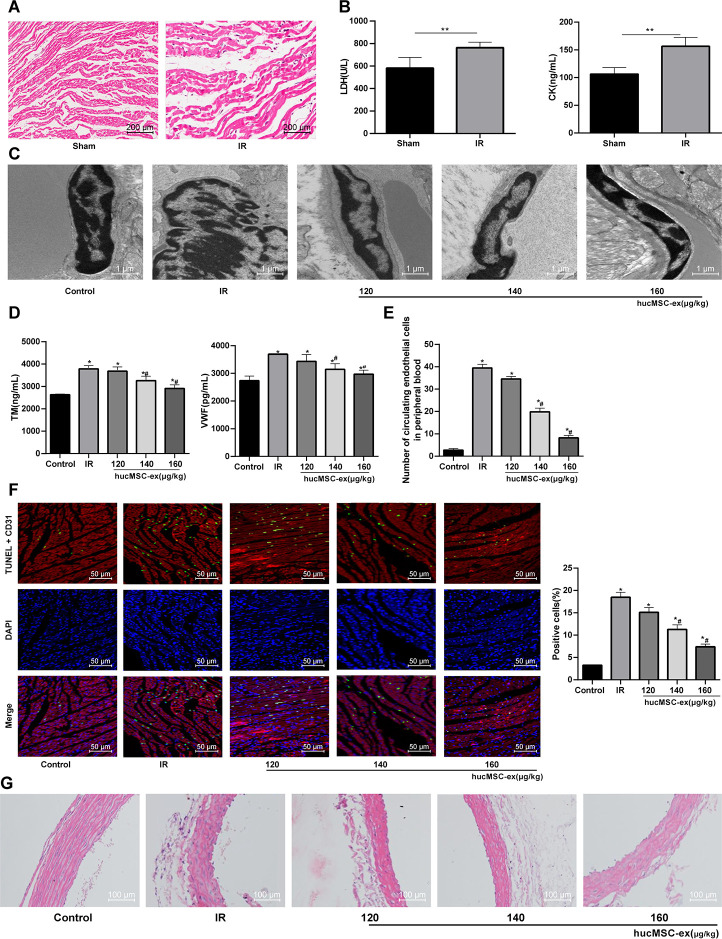
Figure 3.
The hUCMSC-ex protects rats against the I/R injury. (A) HE staining for the detection of myocardial pathological morphology in rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex (n = 3). (B) Levels of cardiac function indexes LDH and CK in I/R rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex measured by ELISA kits (n = 8). (C) Ultrastructure of CMECs in I/R rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex observed under transmission electron microscope (n = 3). (D) Serum TM and vWF levels in I/R rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex measured by ELISA kits (n = 8). (E) The number of CECs in I/R rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex measured by flow cytometry (n = 8). (F) CD31 + TUNEL-positive CMECs in I/R rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex (n = 3). CMECs were red labeled by CD31, TUNEL-positive cells were green, and DAPI was blue. (G) HE staining of arterial intima structure in I/R rats injected with different concentrations of hUCMSC-ex (n = 3). *p < 0.05, vs. the control group; #p < 0.05, vs. the H/R group. All experiments were repeated 3 times. Data in panel (B) were analyzed with independent t test, and data in panels (E, F and G) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and the pairwise comparisons after ANOVA were performed with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.