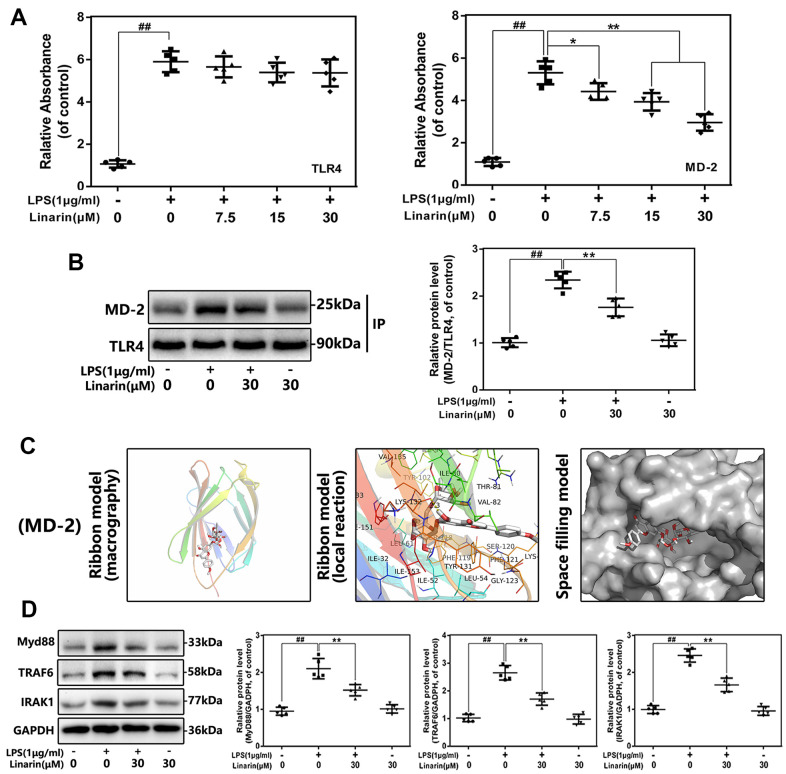
Figure 5.
Influence of Linarin on LPS-induced TLR4/MD-2 signaling activation. (A) The binding of biotin labeled LPS to rhMD-2 and rhTLR4 was examined by competitive ELISA. (B)The complexes of TLR4-MD-2 in chondrocytes treated as above were detected by immunoprecipitation. (C) Linarin was docked with the MD-2 structure. Docking studies were performed as described in Materials and methods. The protein residues are shown in a ribbon model. The proposed binding pose of Linarin shows interactions with LYS-132. The space filling models show the binding of Linarin in the inhibitory binding pockets. (D) The protein expressions of MyD88, IRAK-1 and TRAF-6 in chondrocytes treated as above were detected by western blot. The data in the figures represent the averages ± S.D. Significant differences among different groups are indicated as ##P < 0.01, vs. control group; **P < 0.01 vs. LPS alone treatment group, n=5.