Figure 1.
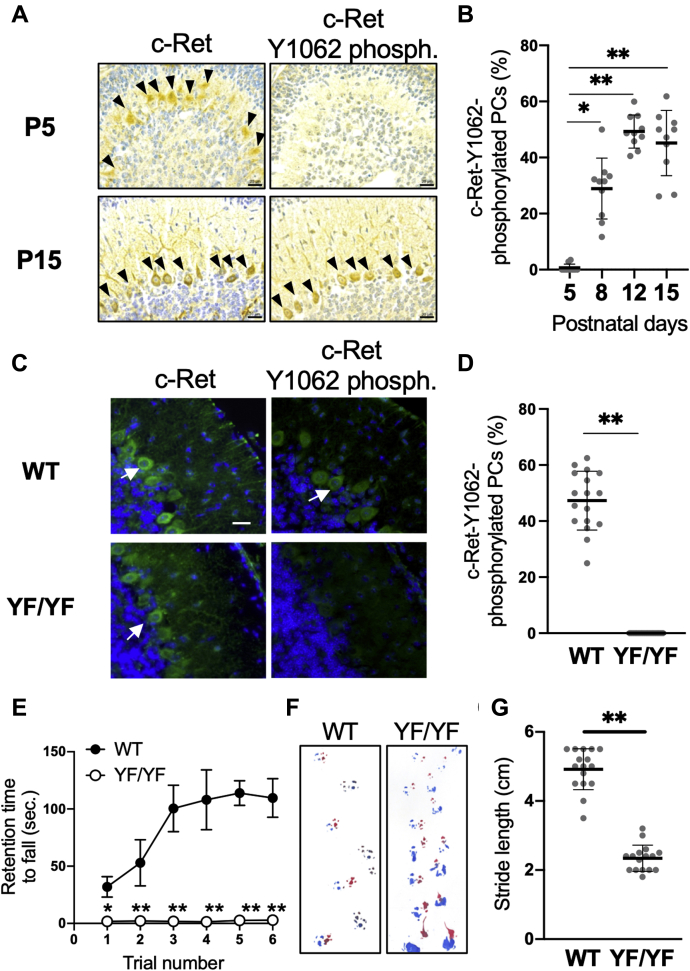
Postnatal increase of c-Ret Y1062-phosphorylated PCs.A and B, c-Ret-expressing (arrowheads in upper panels) and c-Ret-Y1062-phosphorylated (arrowheads in lower panels) PCs from 5, 8, 12, and 15-day-old WT mice. B, percentage (mean ± SD, n = 5) of Y1062-phosphorylated PCs in WT mice. The results of 2–3 serial sections from five mice are shown with dot plots. C, c-Ret-expressing (arrows in left panels) and c-Ret-Y1062-phosphorylated (arrows in right panels) PCs from 14-day-old WT- (upper panels) and YF/YF-mice (lower panels). D, percentage (mean ± SD, n = 4) of Y1062-phosphorylated PCs in 14-day-old WT mice (WT) and c-Ret-KIYF/YF-mice (YF/YF). Scale bars: 20 μm. The results of four serial sections from four mice are shown with dot plots. E, retention times (seconds, mean ± SD) of YF/YF-mice (open circles, n = 7) and littermate WT mice (black circles, n = 7) on the rotarod (at 25 rpm) were recorded. F, footprint analysis. G, quantification of stride length (cm, mean ± SD) of YF/YF-mice (n = 5) and littermate WT mice (n = 5). The results of three trials from five mice are shown with dot plots. Significant difference (∗∗p < 0.01; ∗p < 0.05) from the control was analyzed by the paired t test (B), the Mann–Whitney U test (E) and the unpaired t test (D, G).