FIG 4.
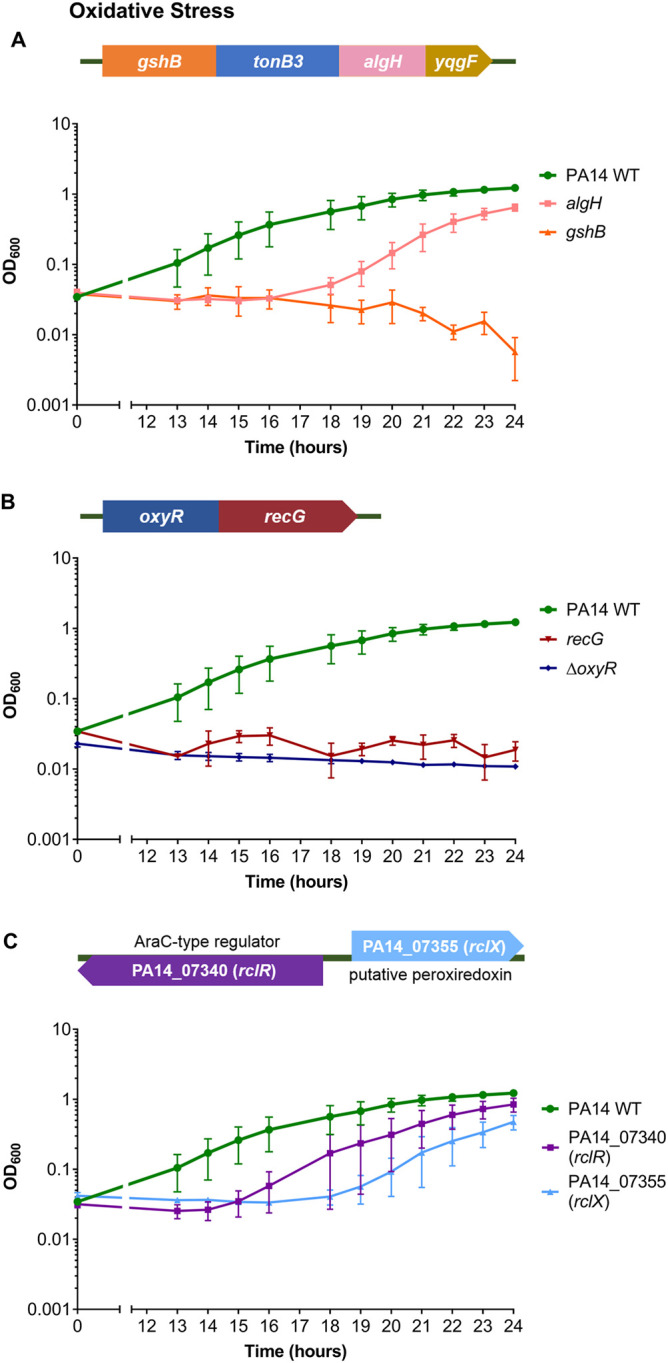
Mutants of genes involved in oxidative stress defense displayed altered susceptibility to HOCl. (A) Gene arrangement of the predicted 4-gene operon, gshB-tonB3-algH-yqgF. Growth of PA14 WT, algH, and gshB strains in the presence of 4.4 mM HOCl. PA14 transposon mutants were not available for yqgF but were for tonB3; however, they did not display altered HOCl susceptibility (data not shown). (B) Gene arrangement of the oxyR-recG operon. Growth of PA14 WT, recG, and ΔoxyR strains in the presence of 4.4 mM HOCl. (C) Gene arrangement of PA14_07340 (rclR) and PA14_07355 (rclX). Growth of PA14 WT, PA14_07340 (rclR), and PA14_07355 (rclX) strains in the presence of 4.4 mM HOCl. Graphs display the means and standard errors of the means for three independent experiments (two independent experiments only for recG). All mutant strains displayed statistically significant altered susceptibility to HOCl compared with the WT at different time points (P < 0.05; one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test). Strains grown in the absence of HOCl showed no growth defects (data not shown). All transposon mutants and the in-frame deletion were confirmed by PCR.
