Figure 2.
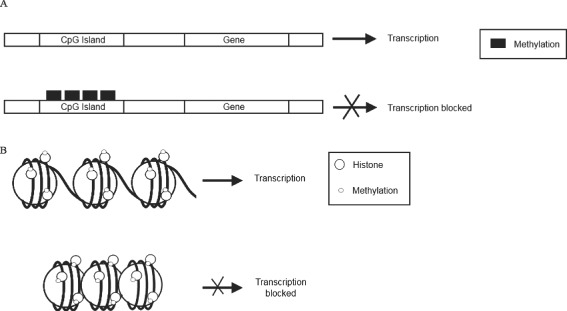
DNA and histone methylation status is important in the regulation of gene transcription during wound healing. The methylation of cytosine and guanine islands (CpG) residues, located in the gene promoter region, results in repressed gene transcription (A). Histone methylation can result in either gene expression or repression, depending on which histone residue has been methylated (B). For example, mono‐, di‐ or trimethylation of histone 3 on lysine residue 4 (H3K4) confers a transcriptionally active chromatin state. An example of this is H3K4me. In contrast, other histone methylation events, such as H3K9me and trimethylation of H3K27 (H3K27me3) are correlated with transcriptionally inactive chromatin.
