Figure 1.
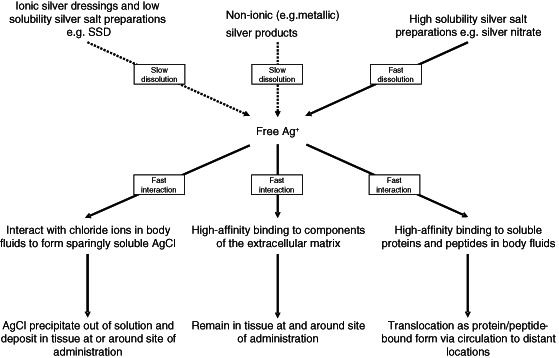
The possible multiple interactions of free silver ions (Ag+) at the site of application. The supply of free Ag+ is from the various silver‐containing products. All common formulations except silver nitrate release Ag+ at low rates of dissolution. Free Ag+ has strong binding reactions with chloride ions in biological fluids [forming silver chloride (AgCl)], and with soluble proteins and peptides in biological fluids and extracellular matrix proteins. These result in the rapid sequestration of silver ions released from dressing formulations into bound forms. Slow release and multiple strong binding reactions all contribute to limit the free Ag+ concentration to very low levels, except when silver nitrate is used – it is highly soluble and can load the site of administration with high levels of Ag+ within a short period of time.
