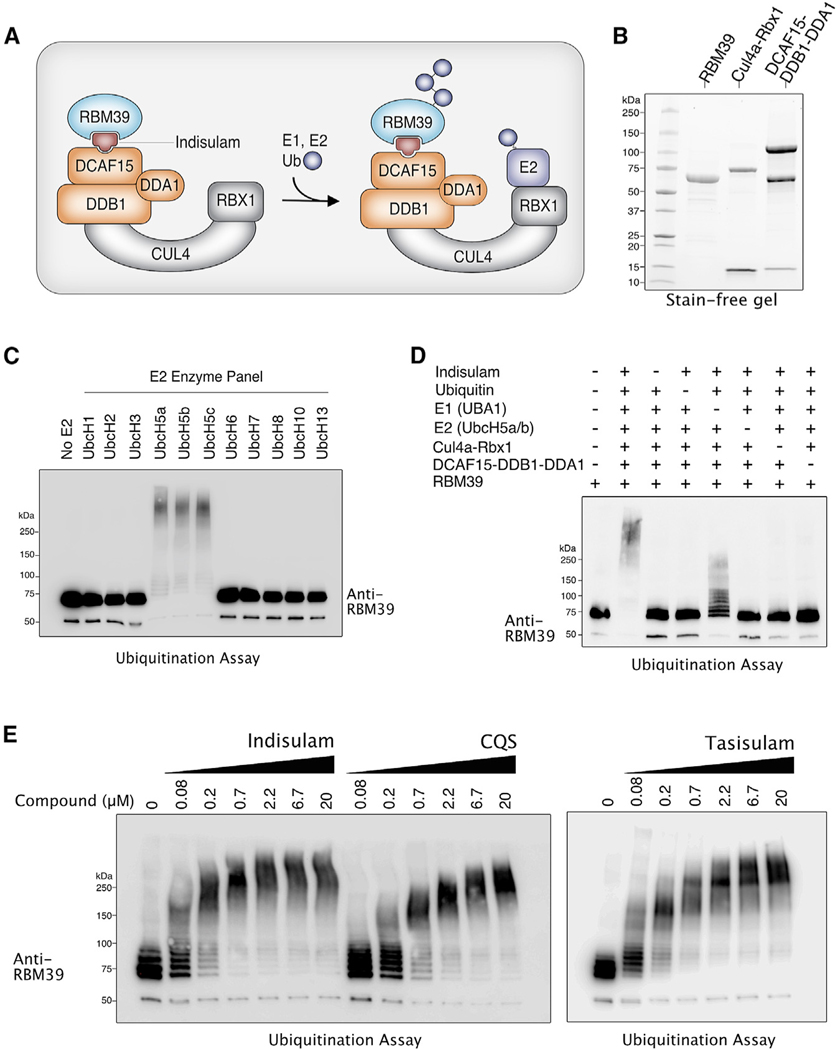
Figure 1. In Vitro Reconstitution of RBM39 Ubiquitination by the CRL4-DCAF15 E3 Ligase.
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating a model of indisulam-dependent ubiquitination of RBM39 by the CRL4-DCAF15 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase.
(B) Stain-free gel of recombinant proteins expressed and purified from SF9 insect cells.
(C) RBM39 can be ubiquitinated in vitro by E2 enzymes UbcH5a, UbcH5b, and UbcH5c. Purified RBM39 was combined with CRL4-DCAF15 E3 ligase complex and screened in a ubiquitination assay against a panel of E2 enzymes (Enzo). Samples were analyzed by western blot with anti-RBM39.
(D) Dropout of individual components of the RBM39 ubiquitination mixture was performed to determine the minimal components required for RBM39 ubiquitination, which was analyzed by western blot with anti-RBM39.
(E) RBM39 ubiquitination in vitro occurs in a dose-dependent manner with the three sulfonamides indisulam, chloroquinoxaline sulfonamide (CQS), and tasisulam.