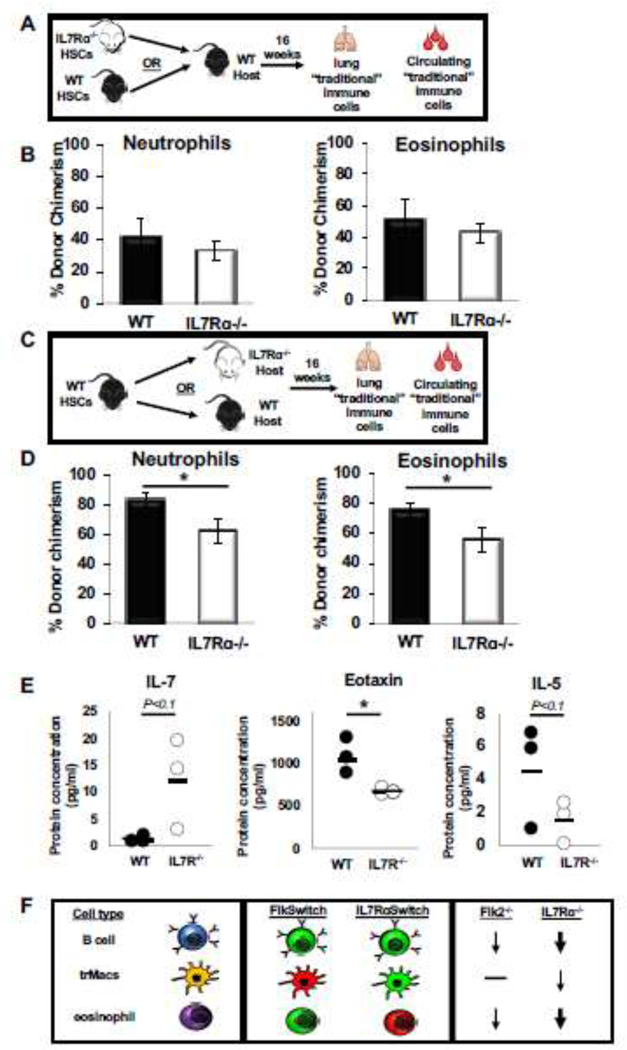
Figure 3: IL7Rɑ is extrinsically required for eosinophil homeostasis in the lung.
A, Schematic depicting the transplantation experimental setup used to determine whether IL7R regulates eosinophil development by cell intrinsic mechanisms. 500 WT or IL7Rɑ−/− HSCs were transplanted into a ¾ sublethally irradiated wild type (WT) GFP recipient. After 16 weeks post transplant, the lungs were harvested and mature immune cells were analyzed via flow cytometry for donor chimerism.
B, IL7R deletion did not alter the ability of HSCs to reconstitute lung eosinophils. Percent donor chimerism of neutrophils and eosinophils in the lungs of transplanted mice. Error bars are SEM, WT n = 4, IL7Rɑ−/− n=6 from 2 independent experiments.
C, Schematic depicting the transplantation experimental setup used to determine whether cell extrinsic IL7R expression is necessary for eosinophil development and homeostasis.
D, WT HSCs were less efficient at generating “traditional” myeloid cells in an IL7Rα−/− host. Percent donor chimerism of neutrophils and eosinophils in the lungs of transplanted mice. Error bars are SEM, WT n = 5, IL7Rɑ−/− n=13 from 4 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.001.
E, Loss of IL7R results in altered cytokine profile in adult mice. Dot plots representing the protein concentration (in pg/ml) of WT (black dots) or IL7Rα−/− (white dots) in the serum of adult mice. Black bars represent the average. WT n=3, IL7Rα−/− n=3 from 3 independent mice; this was sufficient to reach a statistical power of 80% and * P<0.05.
F, Flk2 and IL7R are differentially involved in the development of multiple hematopoietic cell types. Schematic depicting the differential expression and functional requirement for IL7R and Flk2 in traditional lymphocytes (B cells; top), tissue-resident macrophages (trMacs; middle), and adult lung myeloid cells (eosinophils; bottom). Lymphocytes are highly labeled by both Flk2-Cre (FlkSwitch) and IL7R-Cre (IL7RαSwitch), and functionally dependent on both receptors, although more drastic reductions in cell numbers were observed in IL7Rɑ−/− (thick arrow) than in Flk2−/−mice (thin arrow). In contrast, trMacs are highly labeled by IL7R-Cre, but not Flk2-Cre, and functionally rely on IL7R (thin arrow), but not Flk2 (black line), for efficient development. Here, we report that lung eosinophils are highly labeled by Flk2-Cre, but not IL7R-Cre, yet depend on IL7R (thick arrow), but not Flk2 (black line), for efficient maintenance and reconstitution by HSCs.