Figure 2: Targeting OXPHOS and Therapy Resistance in LSCs.
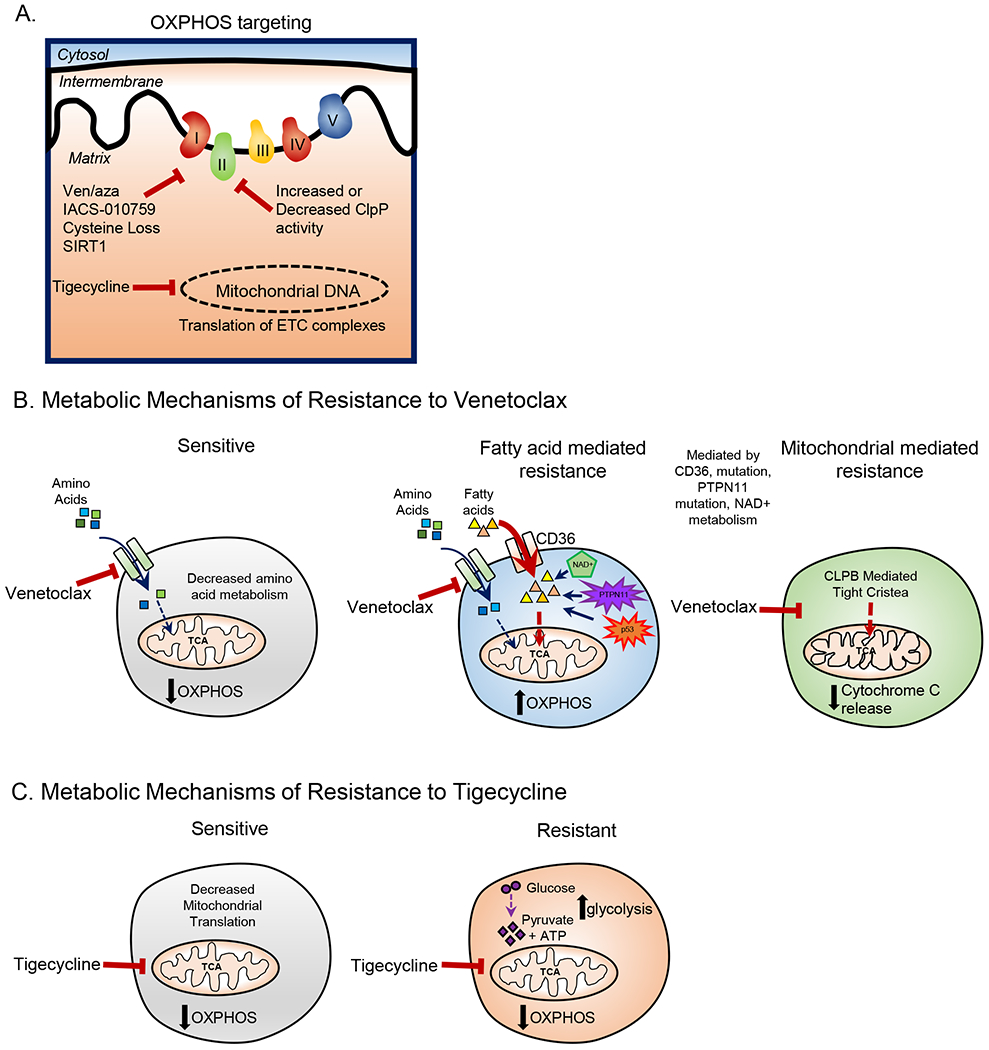
A. OXPHOS in LSCs can be targeted by venetoclax with azacitidine treatment, IACS-010759 treatment, cysteine depletion, ClpP activation or inhibition, inhibition of mitochondrial translation, and SIRT1 deletion. B. In sensitive LSCs venetoclax decreases amino acid metabolism resulting in decreased OXPHOS. Venetoclax resistance in LSCs has been shown to be mediated by increases in fatty acid metabolism which can be caused by increased expression in fatty acid transporter CD36, mutations in TP53, and potentially other mechanisms. Further, venetoclax resistance can be caused by changes in mitochondrial cristae structure which is mediated by CLPB expression. C. In sensitive CSCs tigecycline decreases mitochondrial translation resulting in decreased OXPHOS. Tigecycline resistant CSCs upregulate glycolysis to compensate for the loss of OXPHOS.
