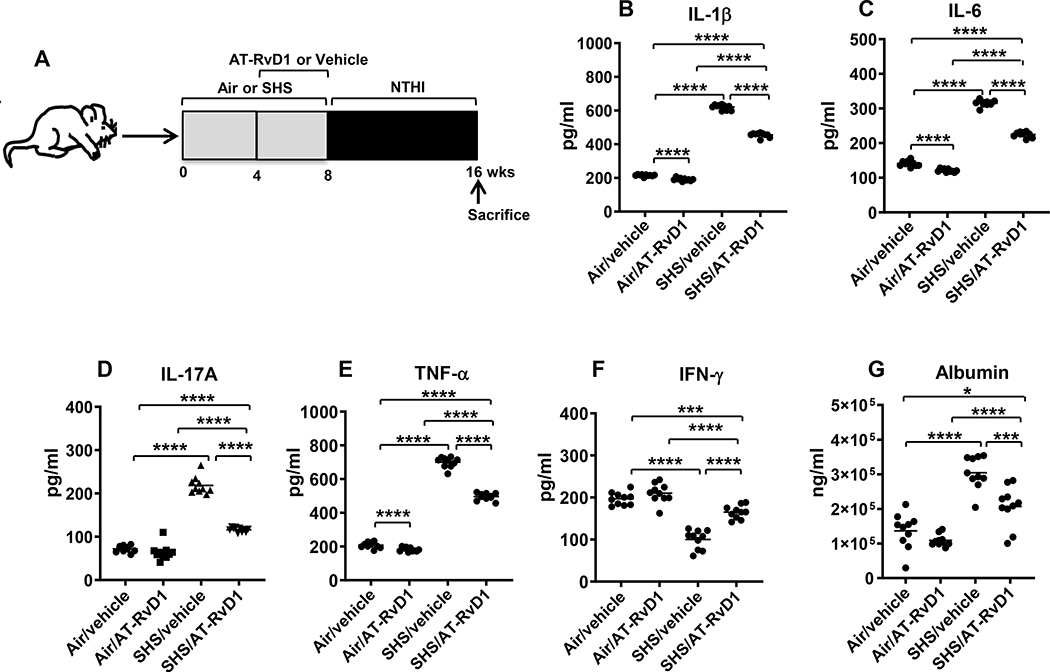
FIGURE 2. AT-RvD1 treatment markedly diminishes SHS-augmented, NTHI-induced proinflammatory cytokine production, reducing SHS-enhanced lung epithelial damage.
(A) C57BL/6J mice were exposed to air or SHS for a total of 8 wks, with or without AT-RvD1 treatment given in the last 4 wks of exposure, and then subjected to chronic infection for an additional 8 wks, as described in material and methods. (B-F) After mice were euthanized, lungs were lavaged and cytokine levels in the BAL were determined by ELISA (n = 10 mice per group). (G) The levels of mouse albumin in the BAL were determined by ELISA as described in methods. Line represents mean value for the group. All treatment groups were performed at the same time, and data show results generated from a single experiment using a total of n=10 mice/group. The results are shown as mean ± SE. Statistical significance between the treatment groups was determined by two-tailed unpaired students t test, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.