Figure 1.
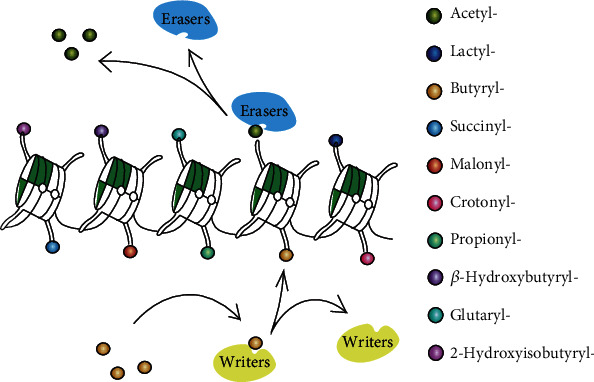
A dynamic process of HPTMs. Histone octamers (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) wrapped around with the double helix make up the core construction of the nucleosome. The addition and removal of HPTMs usually take place on the N-terminal tails of histone catalyzed by specific enzymes called “writers” and “erasers.” The “writers” are enzyme/enzyme complexes that catalyze the covalent modifications of specific residues, and “erasers” are specific enzyme/enzyme complexes that remove the modifications. HPTMs include acetylation, propionylation, butyrylation, 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation, β-hydroxybutyrylation, succinylation, malonylation, glutarylation, crotonylation, and lactylation, which can happen alone or in combination to affect gene expression.
