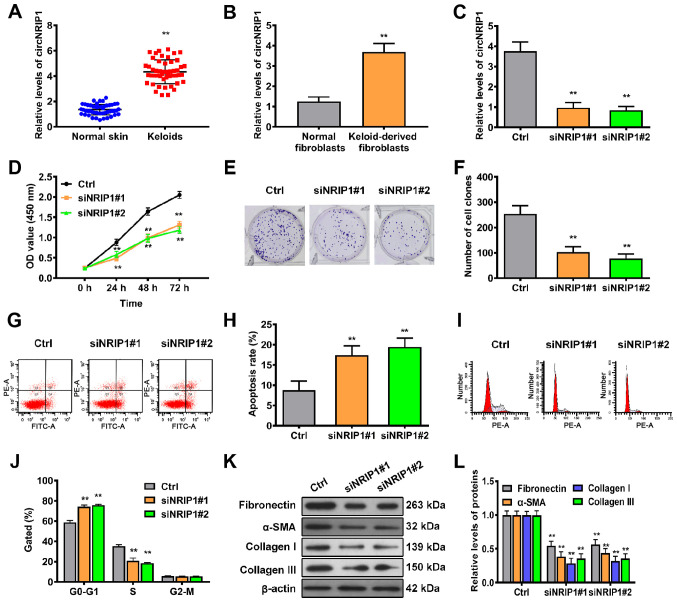
Figure 1.
circNRIP1 is upregulated in keloid tissue and is associated with keloid progression. RT-qPCR assay was performed to detect the abundance of circNRIP1 in (A) keloid and adjacent normal skin tissue and (B) keloid-derived and normal human fibroblasts. (C) Knockdown efficiency of circNRIP1 was evaluated in keloid-derived fibroblasts by RT-qPCR. (D) Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was used to determine the viability of keloid-derived fibroblasts in the presence or absence circNRIP1 knockdown. Colony-forming ability of keloid-derived fibroblasts was (E) assessed and (F) quantified. Flow cytometric assays were conducted to evaluate the effect of circNRIP1 on (G and H) apoptosis and (I and J) cell cycle progression of keloid-derived fibroblasts. (K and L) Changes in the expression of extracellular matrix-associated regulatory proteins in keloid-derived fibroblasts were determined by western blot assay. **P<0.01 vs. Ctrl or human normal fibroblasts. circNRIP1, circular nuclear receptor interacting protein 1; RT-q, reverse transcription-quantitative; Ctrl, control; si, small interfering; OD, optical density.