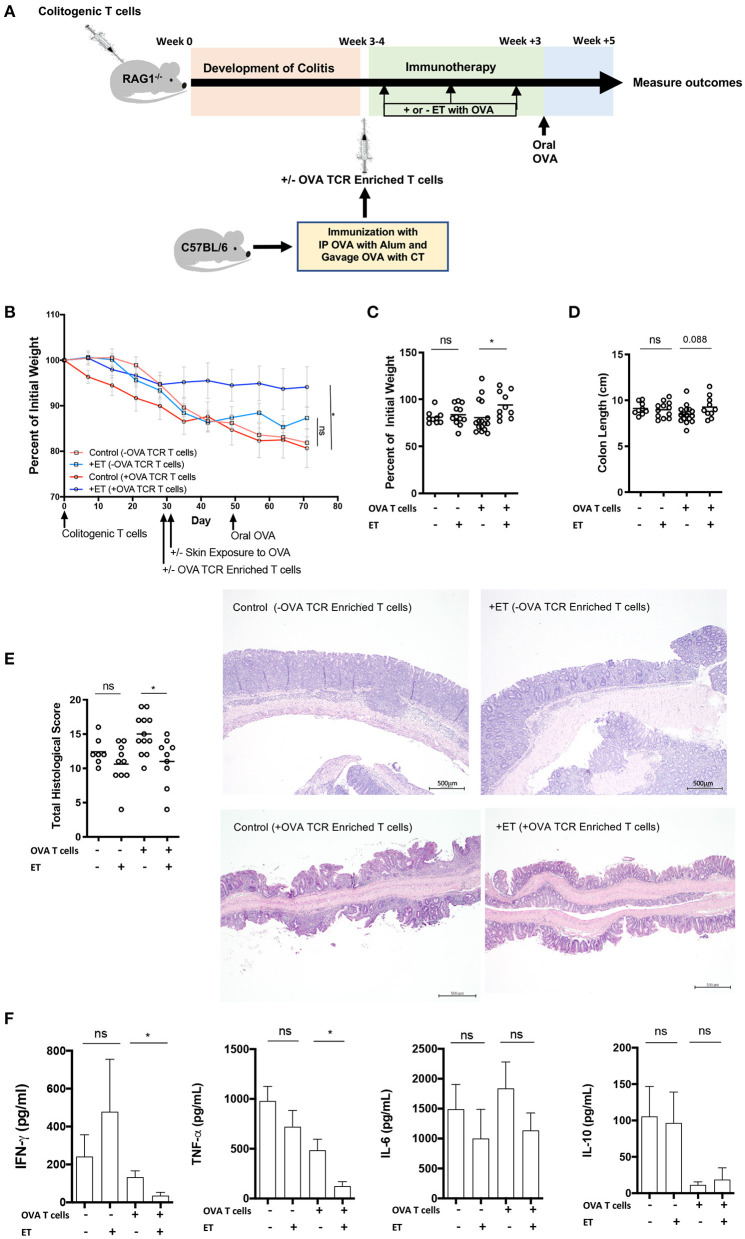
Figure 1.
ET abrogated colitis when OVA TCR enriched T cells from wild-type mice were present but not in their absence. (A) Schematic demonstrating the design of the experiments: ET, Epicutaneous immunotherapy. RAG1−/− mice were injected with colitogenic T cells (CD4+CD45RBhi) from wild-type mice. Once mice exhibited symptoms (weight loss, loose stool, or blood in the stool) of colitis at week 3 or 4, mice were injected or not injected with OVA TCR enriched T cells from C57BL/6 mice that were immunized with IP OVA with alum followed by gavage feeding with OVA with cholera toxin (CT). After this injection, mice were exposed on the skin (+ET) with Viaskin containing OVA or vehicle alone (–ET) weekly for 3 weeks. All mice then received an oral dose of OVA given by gavage. (B) The percentage of initial body weight of mice with colitis with (+OVA T cells) or without (–OVA T cells) the addition of C57BL/6 OVA TCR enriched T cells and exposed to OVA-Viaskin (+ET) or not (control). (C) The final percentage of initial body weight as measured when sacrificing them. (D) Colon length of the mice after sacrificing them. (E) Histological score of colonic tissue as determined by a pathologist blinded to the treatment group. Representative H&E sections of colon at 40× magnification demonstrating the control group that did not receive OVA TCR enriched T cells [control (–OVA TCR Enriched T cells)] and the treated group that did not receive OVA TCR enriched T cells [+ET(–OVA TCR Enriched T cells)] with similar inflammation (total histological scores of 12 and 11, respectively), with diffuse infiltration of the colonic mucosa and expansion of the submucosa by numerous inflammatory cells with necrosis and loss of mucosal epithelium (erosions) and loss of crypts. The inflammatory cells are a mixture of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and lesser numbers of neutrophils. The control sample that did received OVA TCR enriched T cells [Control (+OVA TCR Enriched T cells)] had diffuse infiltration of the colonic mucosa and submucosa by numerous inflammatory cells with loss of mucosal epithelium (erosions), loss of crypts, distortion of the remaining crypts, and a few crypt abscesses. The inflammatory cells are a mixture of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and lesser numbers of neutrophils. The treated sample that received OVA TCR enriched T cells [+ET (+OVA TCR Enriched T cells)] shows multifocal infiltration of the colonic mucosa and submucosa by mild numbers of inflammatory cells composed mainly of lymphocytes and plasma cells. The total histological score of the representative section of control and +ET that received OVA TCR enriched T cells were 14 and 10, respectively. (F) Cytokine production by cultured colon samples (2 pooled experiments of 5–8 mice/group; *p < 0.05; ns, not significant).