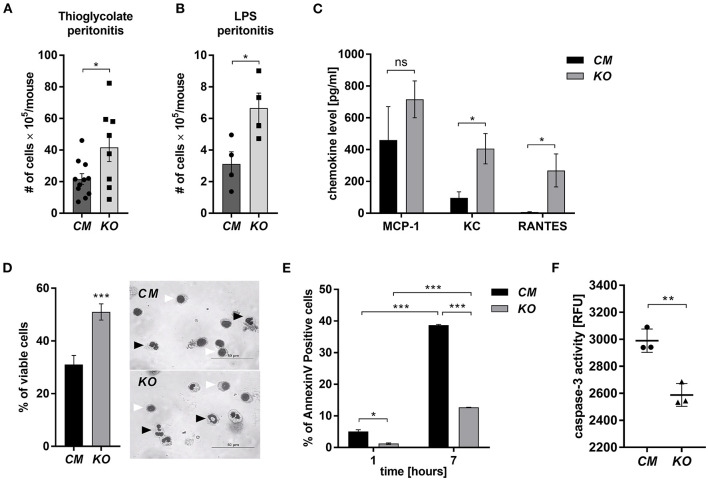
Figure 1.
MCPIP-1 affects neutrophils during inflammation. (A,B) Accumulation of neutrophils in (A) thioglycolate or (B) LPS-induced peritonitis; n = 4–11 (C–F) Neutrophils were isolated from Control Mutant (CM) and Mcpip-1-KO (KO) mice 3 h post i.p. injection with thioglycolate. (C) The chemokine level in the peritoneal fluid was examined using Chemokine Beads Array; the mean ± SEM; n = 4 (D) May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining performed 7 h post isolation of neutrophils. Bars represent the percentage of viable PMNs among 250 counted cells; the mean ± SEM (left). Representative images of stained neutrophils were shown (right)—black-head arrows indicate an example of viable cells, white-head arrows indicate apoptotic cells (E) Neutrophils were double-stained with Annexin V and PI and subjected to FACS. The representative result of Annexin V positive cells was shown; the mean ± SEM. (F) The endpoint values of caspase-3 activity after 15 min of reaction in neutrophils previously cultivated for 7 h. Data show representative RFU changes in time (Relative Fluorescence Unit); the mean ± SEM; n = 3. p-value of < 0.05 (*); p-value of < 0.01 (**); p-value of < 0.001 (***); ns for non-significant.