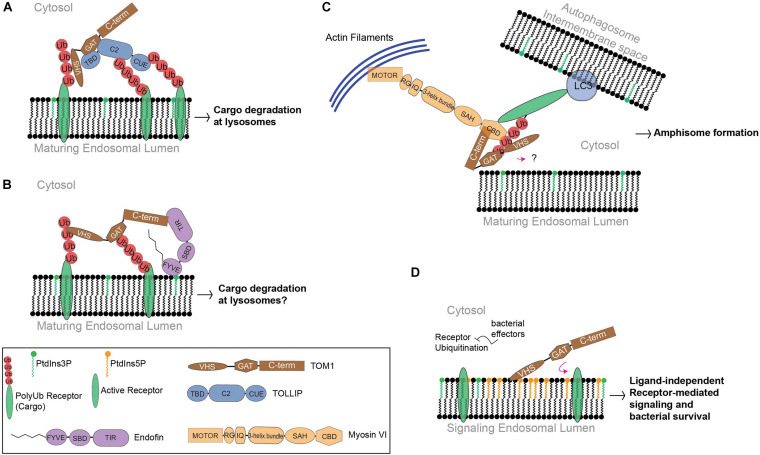
FIGURE 2.
The function of TOM1 in mammals. (A) Cargo is delivered to early endosomes through vesicular transport. TOM1 is recruited by PtdIns3P-bound TOLLIP to these compartments, favoring cargo clustering at maturing endosomes. (B) Endofin recruits TOM1 to early endosomes. Although the function of this complex is unknown, it is possible that it transports cargo for degradation. (C) To mediate amphisome formation, Myosin VI is proposed to bridge endosomal and autophagosomal compartments in coordination with TOM1 and ubiquitinated receptors, which in turn, make contact with the microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3) receptors at autophagosomal surfaces. In this proposed model, TOM1 can also make contact with polyubiquitin chains of receptors through VHS and GAT domains. The contact of TOM1 to endosomal surfaces is unknown. TIR, TOM1-interacting region; SBD, Smad-binding domain; RG, reverse gear region; IQ, isoleucine glutamine motif; SAH, single α-helix region; CBD, C-terminal globular cargo-binding domain. (D) Under bacterial infection conditions, PtdIns5P accumulates at signaling endosomes. Ubiquitination processes are subverted by bacterial effectors. PtdIns5P accumulation favors TOM1 sequestration, which promotes ligand-independent receptor-mediated signaling and cell survival.