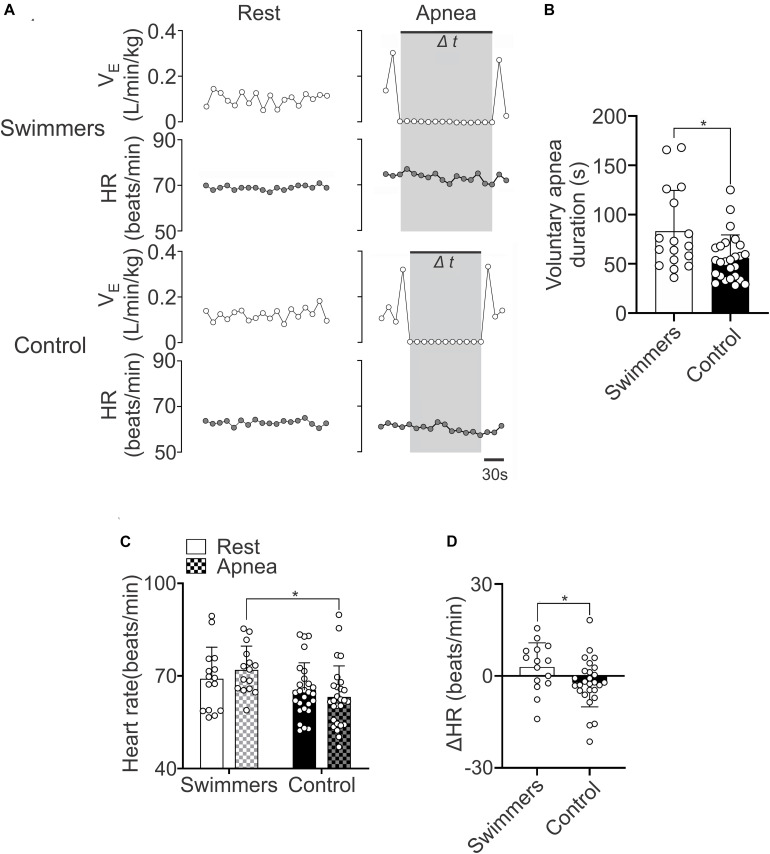
FIGURE 2.
Swimmers are able to maintain longer apnea time and a higher heart rate response during the apnea effort. (A) Representative data of VE and HR of one swimmer and one control participant during rest and maximal voluntary apnea effort. Note that swimmers displayed higher HR responses than controls during apnea test. (B) Summary data of maximal apnea duration. Note that swimmer athletes displayed a marked longer apnea duration compared to control participants. (C,D) Summary results of HR and ΔHR during rest and apnea effort. Note that swimmer athletes displayed a more pronounced positive chronotropic response to a maximum voluntary apnea effort. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Holm–Sidak post hoc test for (C) and unpaired T-test for (B,D). Values are mean ± SD, Swimmers n = 15, Control N = 27. *p < 0.05 compared to Swimmers.