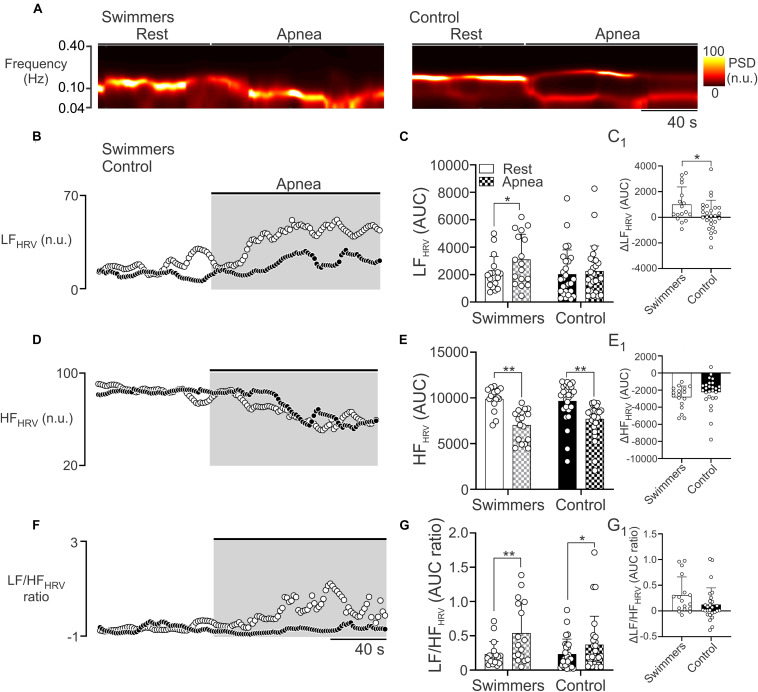
FIGURE 3.
Autonomic control during the maximum voluntary apnea test in swimmers and control participants. (A) Representative time-varying domain spectrum of heart rate variability (HRV) during rest and during the maximal voluntary apnea. Note that swimmers athletes displayed a large increase in the low frequency component of HRV (LFHRV, 0.04–0.10 Hz), concomitant to a decrease of high frequency component of HRV (HFHRV, 0.10–0.40 Hz) following the apnea effort. (B,D,F) Summary data of power spectral density (PSD) of non-stationary analysis of HR with 2-s resolution (time varying domain of HR variability) during the apnea test to LFHRV, HFHRV, and LF/HFHRV ratio, respectively. (C,E,G) Summary data of LFHRV, HFHRV, and LF/HFHRV ratio, respectively, of HRV non-stationary analysis. (C1,E1,G1) Summary data of ΔLFHRV, ΔHFHRV, and ΔLF/HFHRV ratio, respectively. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Holm–Sidak post hoc test for (C,E,G); unpaired T-test for (C1,E1,G1). Values are mean ± SD, Swimmers n = 15, Control N = 27. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.