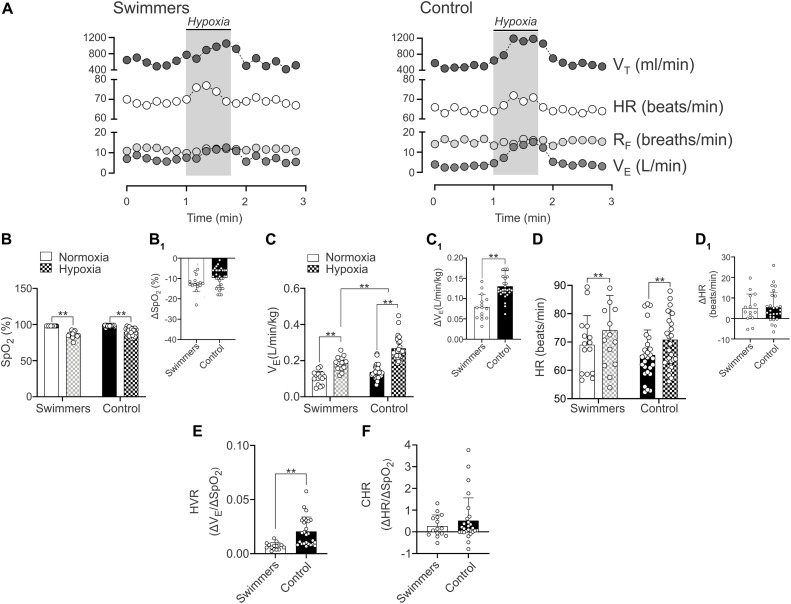
FIGURE 4.
Hypoxic ventilatory (HVR) cardiac (HCR) responses in young trained swimmers. (A,B) Representative data of VT, HR, RF, and VE of one Swimmer and Control participant during a hypoxic challenge (pure N2). Note that swimmers displayed a decrease VE response compared to the control participants. (B,B1) Summary of SpO2 changes in normoxia and hypoxia and summary of ΔSpO2 between normoxia and hypoxia in both groups, respectively. (C) Summary of VE responses to hypoxia of both groups. Note that the breathing response was minor in swimmers compared to the control participants. (C1) Quantification of ΔVE between normoxia and hypoxia in both groups. (D) Summary of HR responses to hypoxia of both groups. (D1) Quantification of ΔHR between normoxia and hypoxia in both groups. (E) Swimmers group showed a significantly lower HVR compared to controls. (F) Summary data of CHR. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Holm–Sidak post hoc test for (B–D); unpaired T-test for (C1); and Mann–Whitney test for (D1,E,F). Values are mean ± SD, Swimmers n = 15, Control N = 27. **p < 0.01.