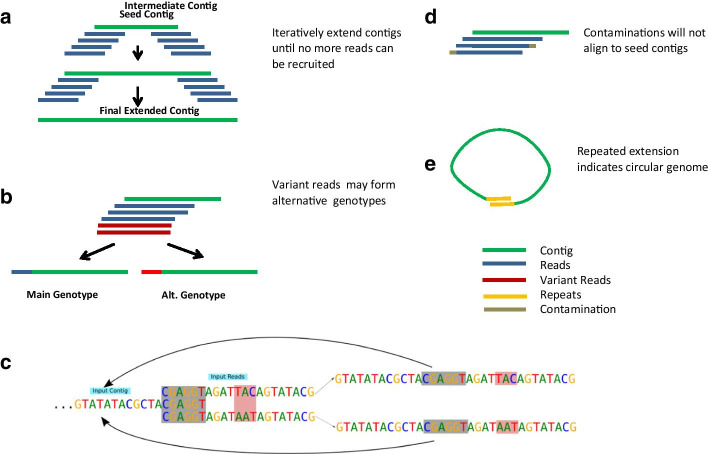
Fig. 1.
Schematic views of the ContigExtender assembly algorithm. (a) Iteratively recruit reads which overlap the edges of input contigs, then generate consensus sequence from the overlaps for form extended contigs. (b) Multiple strains may form alternative consensus contigs. Create branches when variant reads were detected. (c) A more detailed demonstration of the overlapping-consensus-branching algorithm, showing the two branches formed by depth first search (DFS). Two aligned reads have a three base disagreement region, so two different paths are formed for alternative extension. (d) Reads containing untrimmed adapters or other sequencing errors will not align well with contig and other reads. (e) Circular genome detection and extension termination