Figure 6.
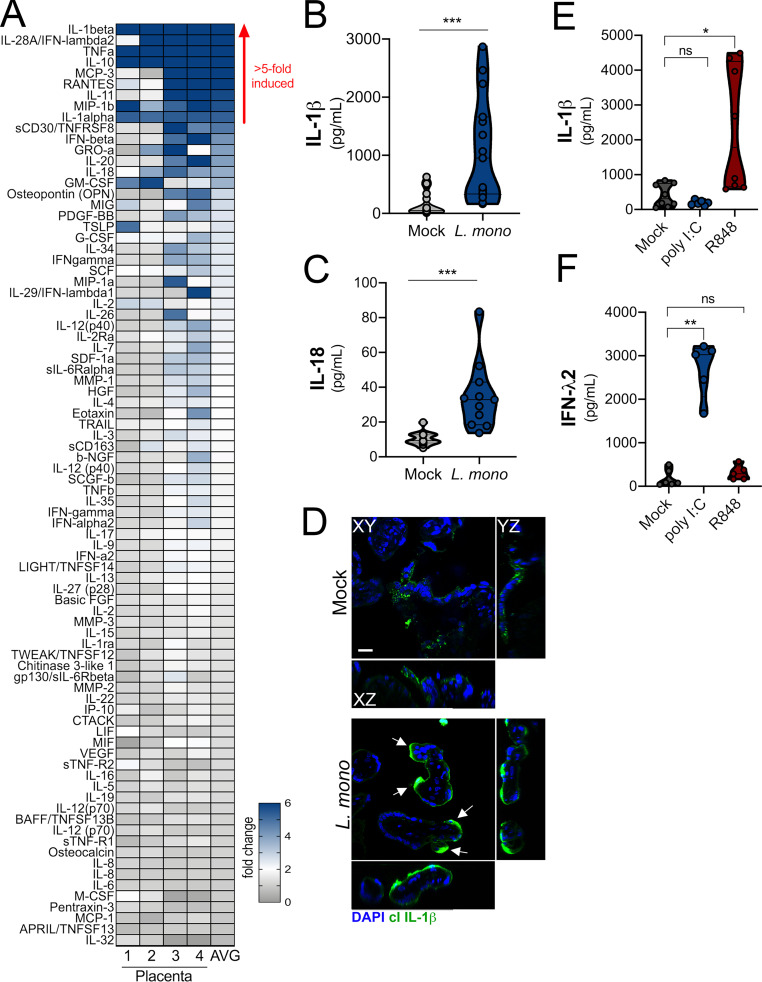
Infection of chorionic villi with L. monocytogenes enhances IL-1β and IL-18 secretion. (A) Heatmap demonstrating the induction (shown as fold change from mock-infected controls) in chorionic villi specimens infected with L. monocytogenes (104 CFU/ml) for 24 h. At least three independent villi from four unique placental preparations were included, and Luminex assay was performed in duplicate. AVG denotes the average change in concentration of cytokines over villi obtained from four placentas. Blue denotes significantly up-regulated factors, and gray or white denotes little to no change (scale at top left). The red arrow demonstrates cytokines with greater than fivefold difference observed in the average of all experiments. (B and C) IL-1β (B) and IL-18 (C) cytokine levels present in CM from chorionic villi samples with or without infection. Symbols represent individual villi from four different placental preparations. (D) Confocal microscopy of cleaved IL-1β (in green) in chorionic villi infected with L. monocytogenes (104 CFU/ml) for 24 h. DAPI-stained nuclei are shown in blue. y–z and x–z cross-sections are shown at right and below. White arrows denote staining in syncytiotrophoblasts. Scale bar is 10 µm. Images are representative of imaging of at least three to five independent fields from three unique placental preparations. (E and F) Levels of IL-1β (E) or IFN-λ2 (F) following exposure of chorionic villi to poly I:C (10 µg), resiquimod (R848; 10 µg), or mock treated as a control for 24 h. Data are from three unique placental preparations with three to five villi used per placenta, with Luminex assay performed in duplicate. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Symbols represent villi (averaged) from individual placental preparations.