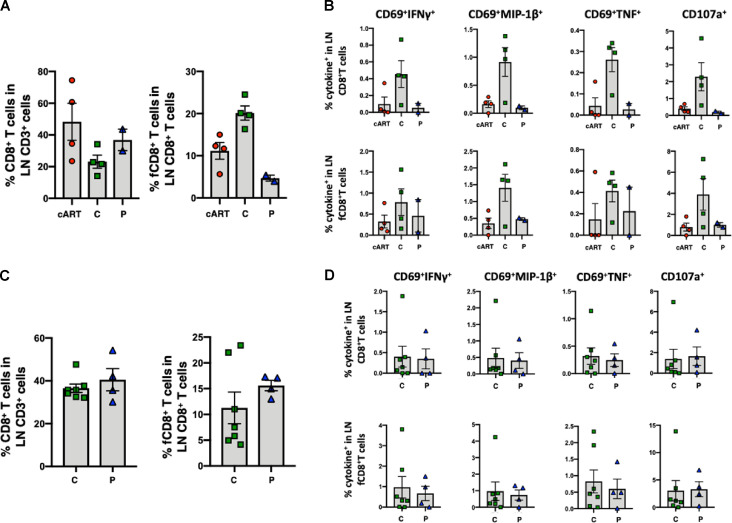
Figure S3.
Follicular CXCR5+ CD8+ T cell accumulation and SIV-specific CD8+ T cell responses in LNs from the controller macaques occur following combination bNAb therapy beginning on day 3 PI, but not in the controller macaques following bNAb ± cART treatment beginning at week 2 PI. (A–D) Treatments were initiated on day 3 (A and B) or at week 2 (C and D). (A) Follicular CXCR5+ CD8+ T cells accumulated in LNs of day 3 controller (C) animals (n = 4) compared with the same T cell subset collected from progressor (P) macaques (n = 2) or control monkeys treated with cART only, starting at day 3 (n = 4). Comparable fractions of bulk CD8+ T cells were present in LNs from the three groups of monkeys. The Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test showed a statistically significant difference in levels of fCD8+ T cells between controller and progressor monkeys (P = 0.0228). (B) Antiviral responses in both bulk and follicular CXCR5+ CD8+ T cells in LNs from controller macaques were higher than in LNs from progressor or cART-only control macaques. The CD8+ T cell responses to SIVmac239 Gag were measured by intracellular cytokine staining (IFN-γ, MIP-1β, TNF, and CD107a). (C) The fractions of follicular CXCR5+ CD8+ T cells in LNs from controller (n = 7) and progressor (n = 4) animals were comparable. (D) Antiviral responses in both bulk and follicular CXCR5+ CD8+ T cells in LNs from controller macaques were comparable to the responses measured in progressor animals. The CD8+ T cell responses to SIVmac239 Gag were measured by intracellular cytokine staining (IFN-γ, MIP-1β, TNF, and CD107a). Error bars indicate SD of data from multiple animals.