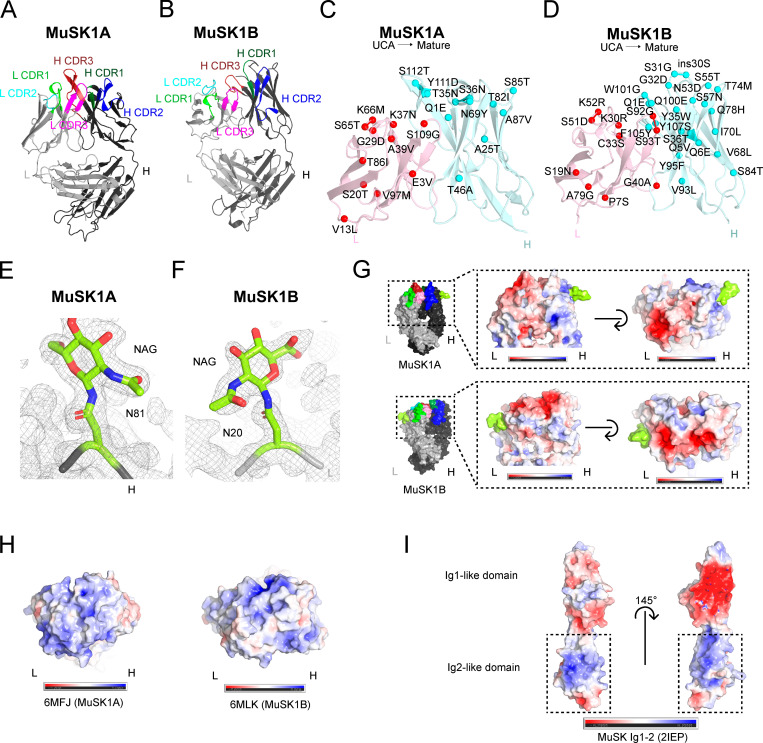
Figure 2.
Crystal structure, mutation map, and glycosylation and electrostatic potential maps of MuSK1A, MuSK1B, and the MuSK Ig1-2-like domain. (A) Structure of MuSK1A heavy and light chains (PDB: 6WYR). (B) Structure of MuSK1B heavy and light chains (PDB: 6WYT). (C) UCA mutations mapped to the mature MuSK1A. UCA mutations are scattered throughout the mature MuSK1A CDR and FR regions. The MuSK1A light chain is colored light pink, and the MuSK1A heavy chain is colored pale cyan. UCA mutant Cα carbons are shown as darker red or cyan spheres for the light or heavy chain, respectively, with the mutation from the UCA to the mature mAb. (D) UCA mutations mapped to mature MuSK1B. UCA mutations are uniformly distributed throughout the mature MuSK1B CDR loops and FR regions. (E) N81 glycosylation site in the MuSK1A heavy chain at a threshold of 1.0 σ in the 2Fo-Fc map. The MuSK1A heavy chain backbone is shown as a black tube. (F) N20 glycosylation site in the MuSK1B light chain at a threshold of 1.0 σ in the 2Fo-Fc map. MuSK1B light-chain backbone is shown as a light gray tube. (G) Electrostatic potential map of MuSK1A and MuSK1B at the antigen-binding site with the modeled glycans shown in yellow green. In MuSK1A, the light chain is predominantly negatively charged, while in MuSK1B, both the heavy and light chains are predominantly negatively charged. (H) Electrostatic potential map of sequence-related Fabs for UCA MuSK1A (PDB code: 6MFJ) and UCA MuSK1B (PDB code: 6MLK) at the antigen-binding site. (I) Electrostatic potential map of the MuSK Ig1-like and Ig2-like domains. The MuSK Ig1-like domain is predominantly negative, while the MuSK Ig2-like domain has two positively charged patches.