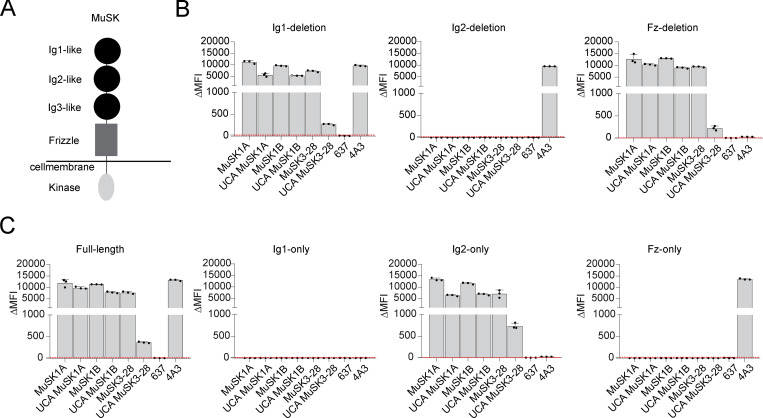
Figure S2.
Mature MuSK mAbs and their UCA counterparts bind to the same MuSK domain. The MuSK mAbs and the UCA were tested for domain binding and recognition with a CBA expressing MuSK-GFP domain variants. (A) Illustration of the full-length MuSK receptor. (B and C) The ectodomain of MuSK consists of several different Ig-like domains and a frizzle domain. Different mutations of the MuSK protein consisting of a domain deletion or specific domain-only construct were tested for binding by the mAbs. Humanized MuSK mAb 4A3 was used as the positive control and AChR-specific mAb 637 as the negative control. Results for each mAb are shown. The ΔMFI was calculated by subtracting the signal from nontransfected cells from the signal of transfected cells. Each bar graph represents the mean value from three independent experiments. Bars represent means and error bars represent SDs. Values greater than the mean + four SDs of the negative mAb 637, indicated by horizontal dotted lines, were considered positive.