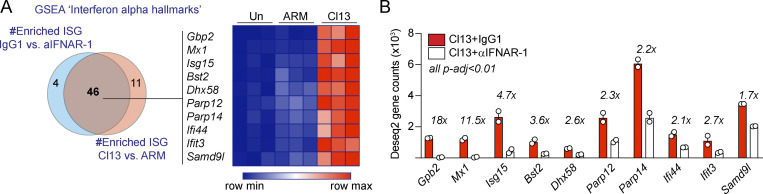
Figure S3.
Antibody-mediated blockade of IFNAR-1 reduces IFN signaling in IECs after LCMV Cl13 infection. C57BL/6 mice were infected with LCMV ARM or Cl13 or left uninfected (Un; A) or injected with isotype (IgG1) or anti-IFNAR-1 Ab (αIFNAR) i.p. (A and B), and RNA-sequencing analysis was performed on FACS-purified IECs at day 9 p.i. (A) Venn diagram (left) shows overlapping GSEA results from the “interferon α hallmarks” gene signature between IEC from Cl13- versus ARM-infected mice and IECs from IgG1- versus anti-IFNAR-1–treated Cl13-infected mice. 10 highly enriched and overlapping ISGs (i.e., highest rank metric scores, FDR < 0.1) were selected for the heatmap (right) depicting Z-scores computed from DESeq2 normalized counts (Table S2, Table S5, and Table S7). (B) Fold reduction in the expression of selected ISG in IECs from IgG1-treated versus anti-IFNAR-1–treated Cl13-infected mice is shown. Averages ± SEM are shown. FDR-adjusted P values (p-adj) were computed by DESeq2.