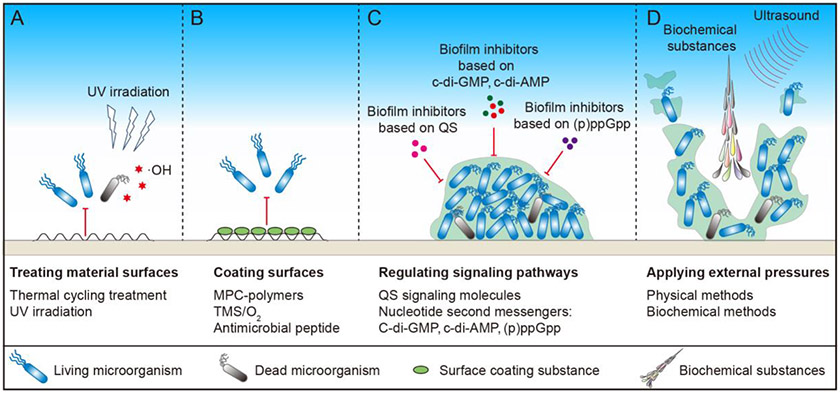
Figure 2. Strategies for controlling harmful biofilms.
(A) Material surfaces can be treated through thermal cycling and UV irradiation. (B) Surfaces can be coated by 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC)-polymers, trimethylsilane (TMS)/O2, and antimicrobial peptides. (C) Biofilm formation can be inhibited by chemical agents that influence quorum sensing (QS), c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP, and (p)ppGpp related pathways. (D) External force, including biochemical substances and ultrasound, can also be applied to eradicate mature biofilms.