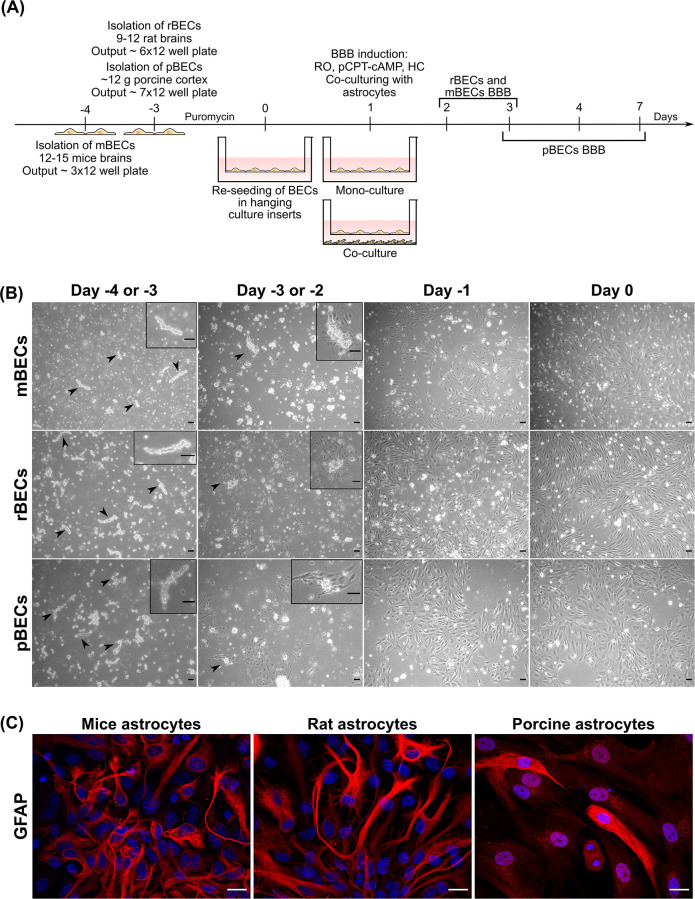
Fig 1. Overview of the construction of the different in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) models.
(A) Mouse brain capillary endothelial cells (mBECs) are isolated on day -4, while both rat BECs (rBECs) and porcine BECs (pBECs) are isolated on day -3. The BECs are grown in a medium containing puromycin until day 0, to secure a pure BECs culture. On day 0, the cells are re-seeded on collagen IV/fibronectin-coated hanging culture inserts. 24 hours later, the BBB properties are induced by the addition of RO 20–1724 (RO), 8-(4-Chlorophenylthio)adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate sodium salt (pCPT-cAMP), and hydrocortisone (HC), and the BECs are subsequently cultured as mono-culture or in co-culture with astrocytes isolated from mice, rat, or porcine brains. (B) Phase-contrast images of the isolated microvessels from day -4 or -3 to day 0 for mBECs, rBECs, and pBECs. The isolated microvessels (arrowheads and boxes) are recognized as small pearls on a string. After 24 hours the BECs start to proliferate from the microvessels, which is highlighted in the box and by the arrowheads. The cells reach a confluence level of 80–90% on day 0. Scale bar = 20μM. (C) Immunofluorescent images of the primary astrocyte cultures isolated from mouse, rat, and porcine brains used for the creation of co-cultures. The astrocytes express the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; red), though at varying intensity, confirming the presence of astrocytes in these cultures. The nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20μM.