Fig. 6. M6T induce the in vivo infiltration and neuroprotection function of macrophages with the increased expression of microglia-specific genes.
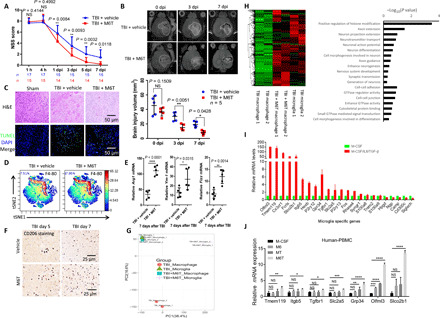
TBI mice were treated with vehicle or M6T to assess NSS [(A) Mann-Whitney U test) or the brain injury volume by MR [(B) two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). At the sites of injury, brain damage and cell apoptosis by H&E staining and TUNEL staining at 3 dpi (C), the percentage of F4/80+ macrophages by CyTOF (D), the mRNA levels of Arg1, Ym1, and Fizz in the isolated CD11b+ cells at day 7 (n = 5) (E), and the numbers of CD206+ cells by immunohistochemistry staining (F) were examined. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (G and H) The irradiated recipient mice were transferred with tdTomato+ BM cells, followed by TBI with or without M6T treatment. F4/80+ tdTomato+ infiltrating macrophages versus F4/80+ local microglia were sorted for RNA-seq. The differentially regulated genes in a heatmap and a GO pathway enrichment analysis were shown. (I) The relative expression of the microglia-specific genes was analyzed from the RNA-seq data in Fig. 5C. (J) Human PBMCs were stimulated with M-CSF, M6, MT, or M6T for 7 days to measure expression of the microglia-specific genes (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, n = 4). tSNE, t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding; PC, principal component.
