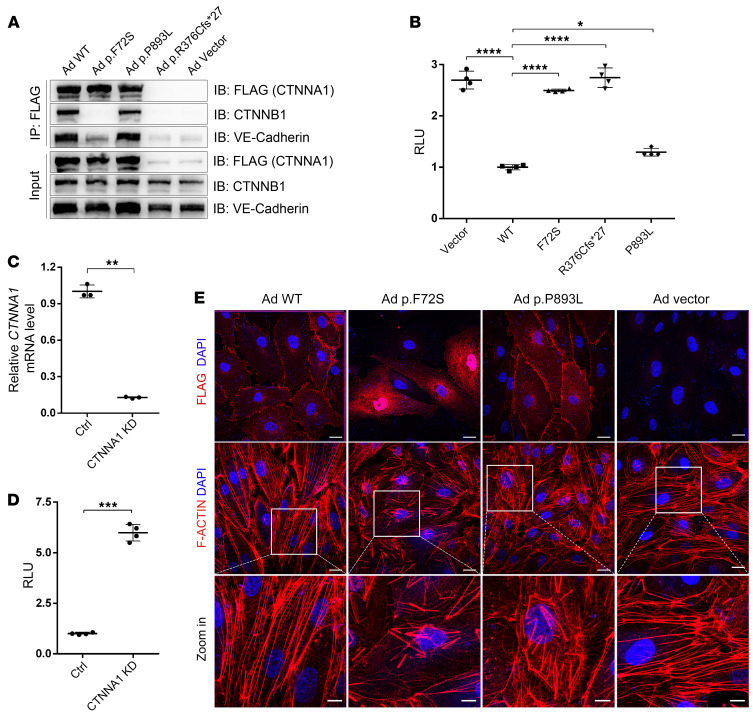
Figure 2. CTNNA1 mutations result in Norrin/β-catenin signaling overactivation, α-catenin mislocalization, and F-actin disorganization.
(A) Western blot analysis of CTNNA1 (WT and mutants) coimmunoprecipitated with CTNNB1 and VE-cadherin. An empty vector was used as a negative control. (B) Results of a luciferase reporter assay in HEK293 STF cells. Cells were transfected with plasmids containing CTNNA1 (WT, p.F72S, p.R376C*fs27, or p.P893L) or an empty vector (pCDNA3.1). Plasmids were cotransfected with LRP5, FZD4, NDP, and Renillareniformis (PGL4.1). The activity of WT protein was normalized to 1. Error bars indicate the SD. *P < 0.05 and ****P < 0.0001, by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (n = 4). (C) qPCR analysis demonstrated efficient shRNA-mediated KD of CTNNA1 in HEK293 STF cells. Error bars indicate the SD. **P < 0.01, by Student’s t test (n = 3). (D) ShRNA-mediated KD of CTNNA1 in the HEK293 STF cell line led to elevated luciferase activity. Error bars indicate the SD. ***P < 0.001, by Student’s t test (n = 4). (E) Adenovirus-mediated (Ad-mediated) overexpression of WT and mutant CTNNA1 (F72S, P893L) in HRECs. Costaining with DAPI and anti-Flag (CTNNA1) or F-actin antibody was performed. Scale bars: 25 μm and 10 μm (enlarged insets). Experiments were performed independently at least 3 times.