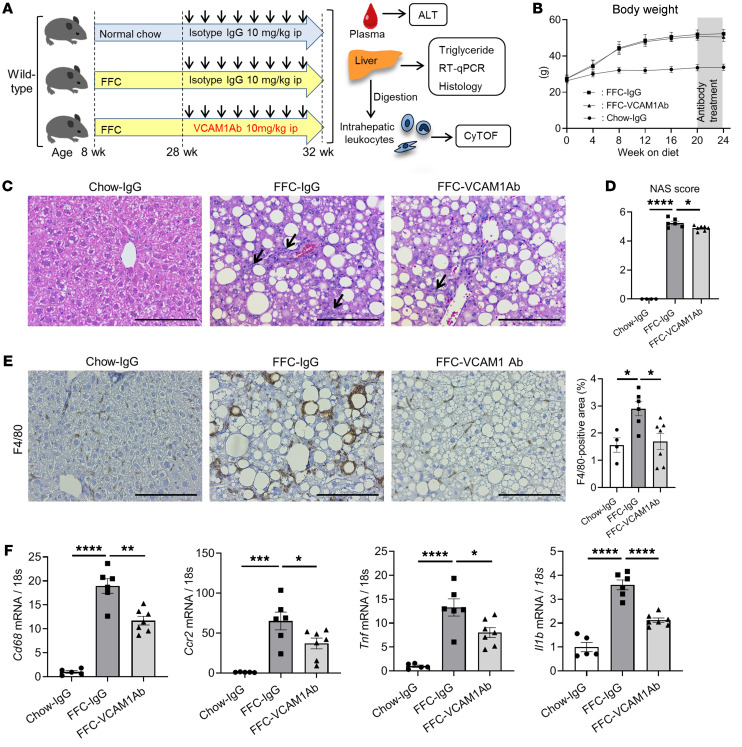
Figure 5. Anti-VCAM1Ab treatment in FFC-fed mice attenuates hepatic inflammation.
Eight-week-old WT C57BL/6J mice were fed either chow or FFC diet for 24 weeks to induce NASH and treated with either anti-VCAM1Ab or control IgG isotype Ab (IgG) twice a week for the last 4 weeks. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental model. (B) Body weight. (C) Representative images of H&E staining of liver tissues. Scale bars: 100 μm. Arrows indicate inflammatory cell infiltrate. (D) NAS. (E) Representative images of F4/80 staining of liver sections (left). Scale bars: 100 μm. F4/80-positive areas were quantified in 10 random ×10 microscopic fields and averaged for each animal (right). (F) Hepatic mRNA expression levels of Cd68, Ccr2, Tnf, and Il1b were assessed by real-time PCR. FC was determined after normalization to 18S rRNA and expressed relative to chow-IgG mice. (B–F) n = 5 to 7 per group; graphs represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison.