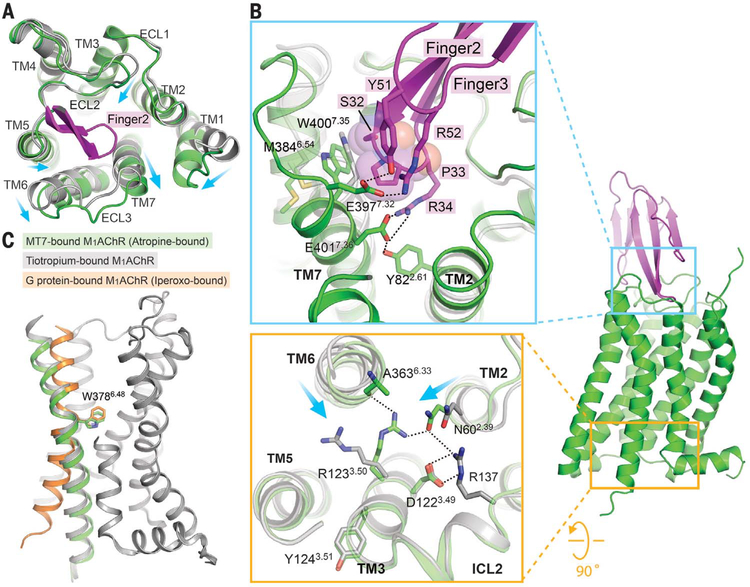
Fig. 2. Conformational changes in M1AChR stabilized by MT7 binding.
(A) Superposition of tiotropium-bound M1AChR (gray; PDB ID 5CXV) and atropine-bound M1AChR-MT7 complex (green) from the extracellular view. Part of finger loop 2 that interacts with TM7 is shown (magenta). Conformational changes are shown with arrows. (B) (Top) Insertion of finger loop 2 stabilizes conformational changes at the extracellular side of TM2, TM6, and TM7. Note that P33 from MT7, represented as spheres, stabilizes W400 outward. (Bottom) Differences in the organization of the DRY motif in the M1AChR-MT7 complex compared with that of tiotropium-bound M1AChR. Displacements of TM helices 2 and 6 are shown with arrows. (C) Conformational change of TM6 between different states of M1AChR, with W378 serving as a pivotal position: M1AChR from the M1AChR-MT7 complex (green); M1AChR from the tiotropium-bound inactive state (gray; PDB ID 5CXV), and M1AChR from the M1AChR-G11 complex (orange; PDB ID 6OIJ).