Fig. 1. Hydrolysis pathways of fumarates.
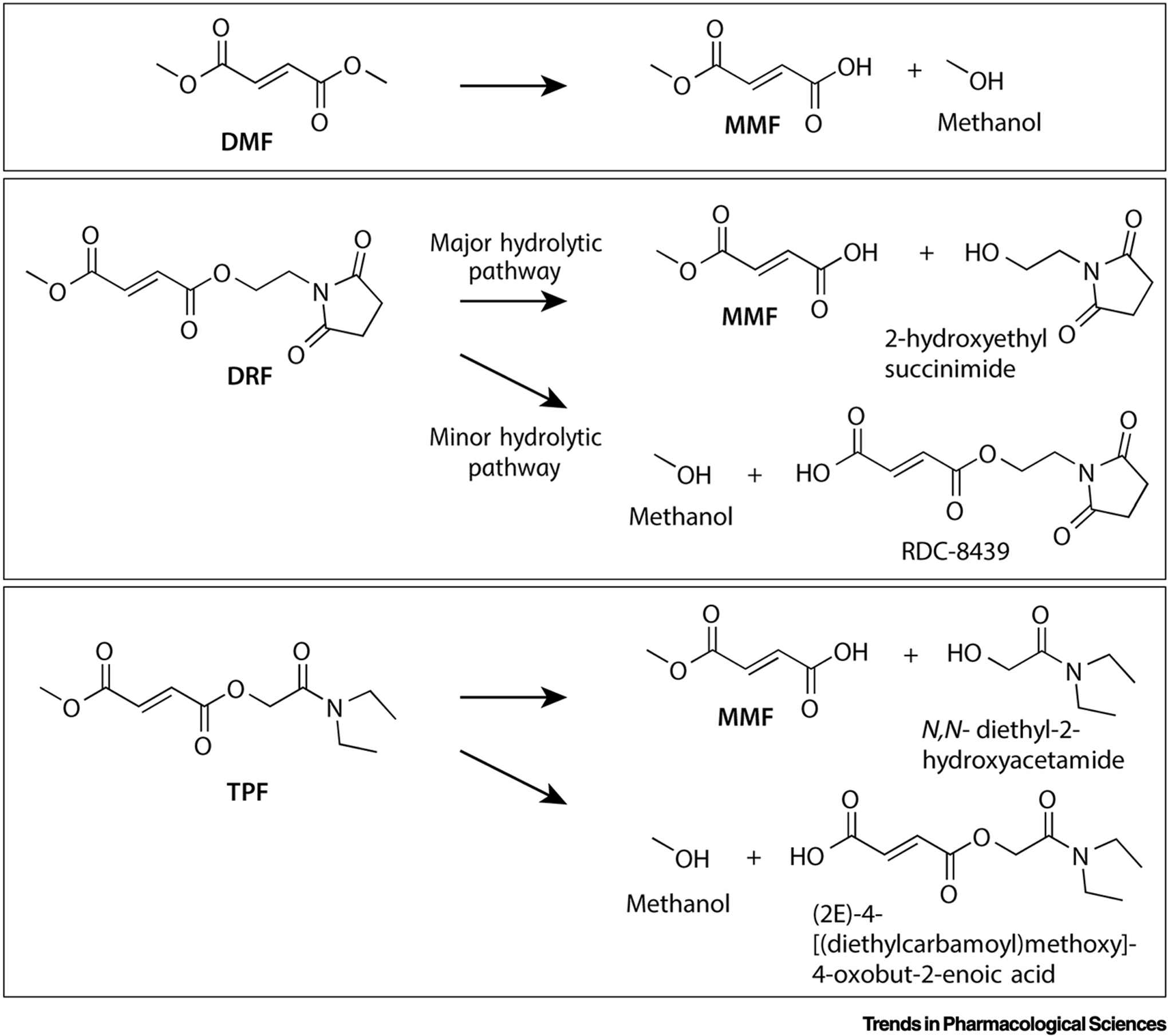
MMF is the major metabolite, along with the cleaved prodrug fragments methanol (DMF), 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide (DRF) and N,N-diethyl-2-hydroxyacetamide (TPF). DMF is a symmetrical diester and leads solely to MMF and methanol. For DRF, 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide and methanol formation occurs asymmetrically in a 9:1 ratio [18]. The biologically inert 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide is eliminated primarily through the renal system (58–63%) and the small amount of RDC-8439 formed is presumably converted to FA and 2-hydroxyethyl succinimide in the liver [17]. It is expected that TPF undergoes similar asymmetric cleavage and clearance, given its bioequivalent MMF production (Table 1), even though its spontaneous hydrolysis is not asymmetric [19].
