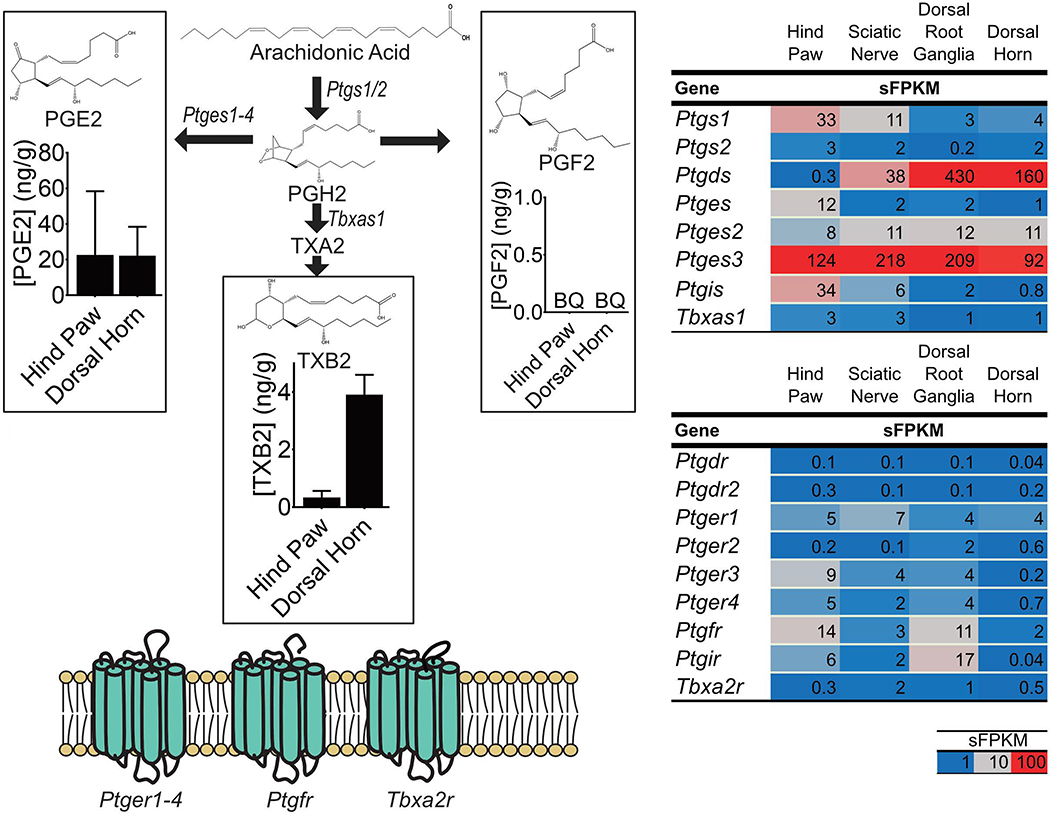
Figure 4: Concentrations of specific prostanoids and expression of genes involved in their synthesis and signaling.
(Left Side) Prostanoids are synthesized by a series of steps starting with the action of Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthases (Ptgs1 and 2) on unesterified arachidonic acid (AA). The product of this reaction is Prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) which is subsequently converted, by specific enzymes to prostanoids such as Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), Prostaglandin F2 (PGF2) and Thromboxane A2 (TXA2). TXA2 is rapidly converted to Thromboxane B2 (TXB2). (Right Side) Expression of genes coding for enzymes involved in prostanoid synthesis as well as for prostanoid receptors, in pain circuit tissue, are presented as sFPKM (mean, n=3). (Left Side Graphs) Concentrations of prostanoid that were detected using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry are presented as median ± interquartile range (ng/g tissue, n=4). Prostanoids were only measured in the unesterified pool.