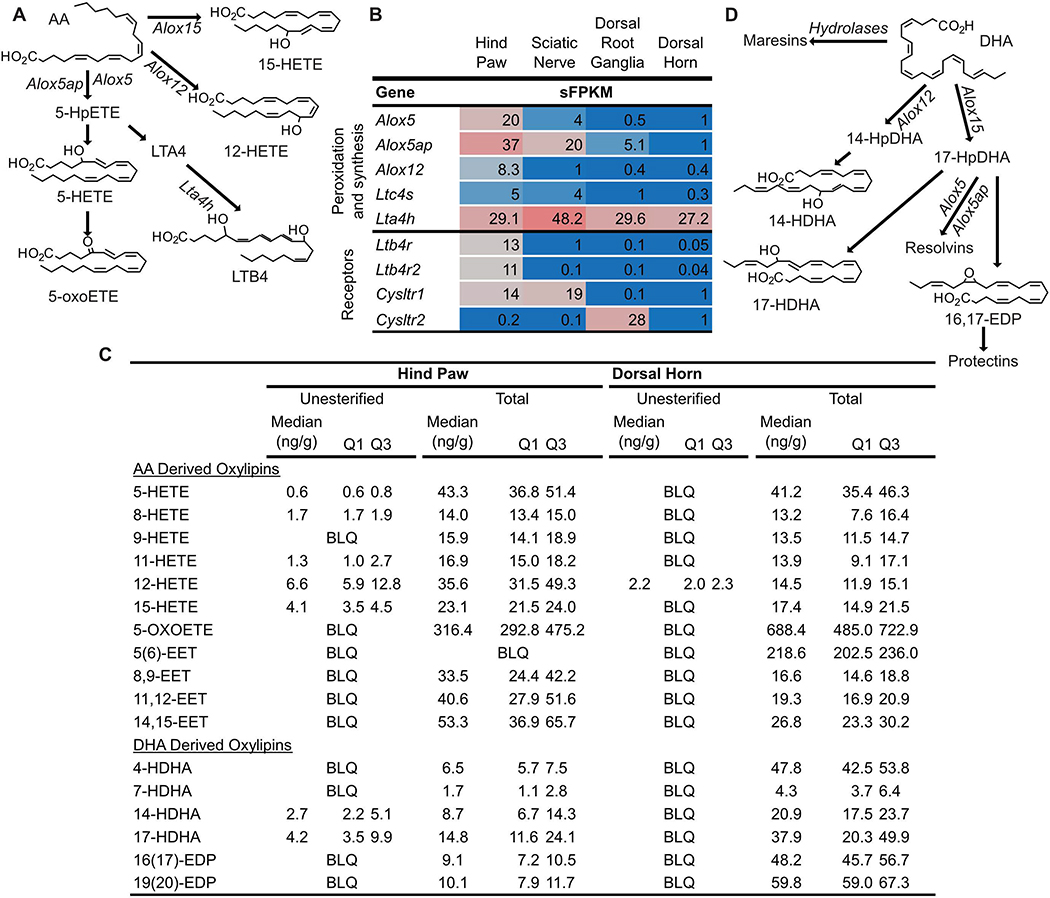
Figure 5: Synthesis pathways and concentrations of Arachidonic acid (AA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) derived oxylipins.
(A) Arachidonate lipoxygenase (Alox) enzymes act on AA to generate hydroperoxy-AA derivatives (HpETEs) which can be rapidly reduced to monohydroxy-AA derivatives (HETEs). Subsequent action of Alox enzymes on HpETEs leads to the generation of leukotrienes (i.e. Leukotriene B4, LTB4) and lipoxins (not shown). Additionally, HETEs can be oxidized to form keto-AA derivatives such as 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxoETE). (B) Genes coding for Alox enzymes as well as other enzymes involved in specific mediator synthesis (i.e. Leukotriene A 4 hydrolase, Lta4h) were expressed in tissue specific profiles in pain circuit tissue (mean sFPKM). (C) Several unesterified HETEs and HDHAs were detected in rat hind paw, but not rat dorsal horn. (D) The same enzymes that synthesize AA derived oxylipins can act on DHA to form hydroxy- and epoxy-DHA derivatives (HDHAs and EDPs, respectively) as well as specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (Resolvins, Maresins and Protectins). (C) Almost all AA and DHA derived oxylipins measured, including epoxy-AA derivatives (EETs) that are generated by the action of cytochrome p450 enzymes on AA (pathway not shown) were present in the total lipid pool of hind paw and dorsal horn. Baseline oxylipins concentrations are expressed as median with quartile 1 (Q1) and quartile 3 (Q3) in ng/g tissue (n=4). BLQ indicates the concentration of that oxylipin was below the limit of detection.