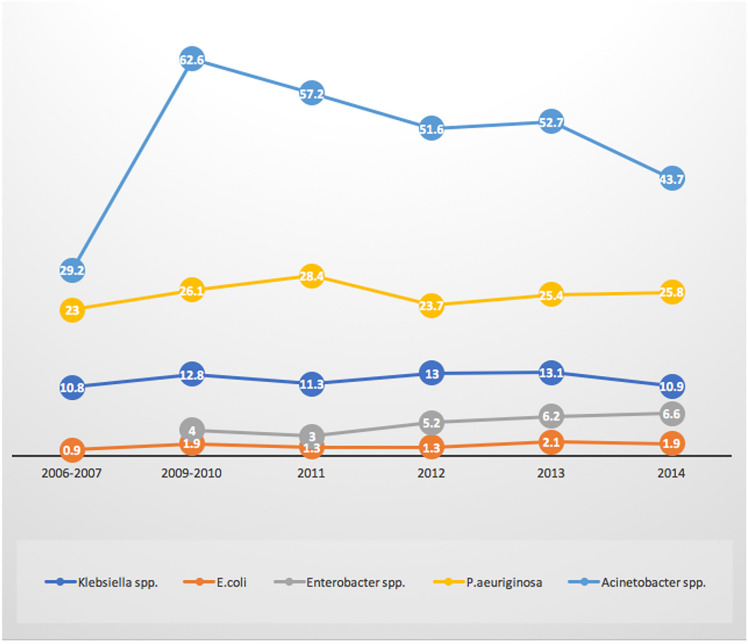
Fig. 2.
Carbapenem resistance from Central Line–Associated Bloodstream Infections (CLABSIs). Figure
adapted from Sievert et al. [32]; values represent percent carbapenem resistant for respective bacteria isolated from postive blood cultures representative of CLABSI infection. Carbapenem resistance, as defined in this report, included all applicable pathogens with a result of I or R to imipenem, meropenem, or doripenem. 2006–2007 Klebsiella data inclusive of K. pneumoniae isolates only. Carbapenem resistance rates by pathogen differ depending on the site of infection [33][34]. Rates for P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii are lower for bloodstream infections that have been reported from other types of infections [e.g., ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)] [32][34] Thus, it is likely that studies reporting bloodstream and CLABSI infections may under-report true prevalence of carbapenem resistance rates