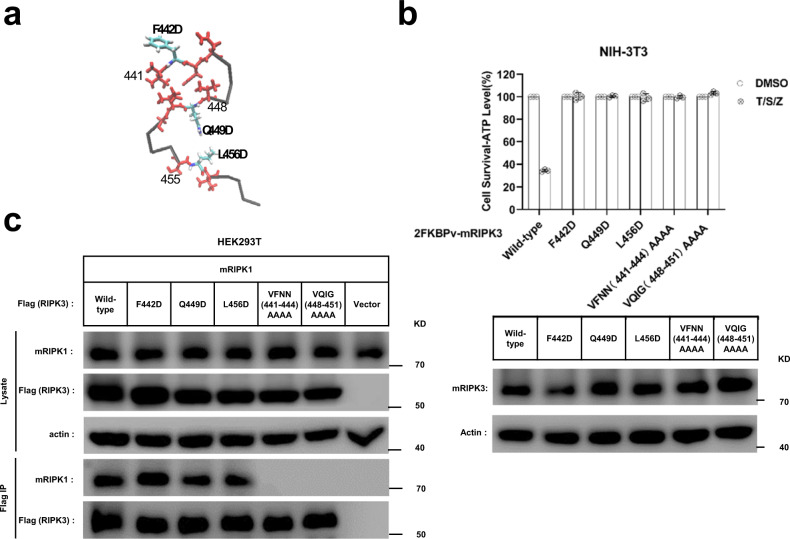
Fig. 7. Cell-based functional assay.
a The monomer structure of mouse RIPK3, showing the three β-strand segments in red and three single mutation sites. b Mutation of F442, Q449, or L456 to D, or quadruple alanine mutations of 441VFNN444 or 448VQIG451 in RIPK3 led to the complete disruption of the TNF-induced cell necroptosis. The NIH-3T3 cells infected with lentivirus containing FKBPv fused wild-type or mutant RIPK3 were treated with TNF-α/Smac/z-VAD (T/S/Z) 10 h. The number of surviving cells were determined by measuring ATP levels using Cell Titer-Glo kit (upper). Data are presented as mean ± SD of n = 3 biologically independent replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Aliquots of 20 μg whole-cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western-blot analysis of mouse RIPK3 and β-Actin which was shown as a loading control (lower). c The RIPK3 mutant F442D, Q449D, L456D did not affect the interaction between mouse RIPK1 and mouse RIPK3. The HEK293T cells were co-transfected with DNA plasmids containing mouse RIPK1 and Flag-tagged mouse RIPK3 (or its mutants). Cell lysates were collected 36 h post transfection, and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag magnetic beads (Bimake) at 4 °C. The total cell lysates and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western-blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. All experiments were repeated three times. The following antibodies were used in this study: anti-mRIPK3 (Sigma-Aldrich, PRS2283, 1:3000); anti-RIPK1 (Cell Signaling Technology, D94C12, 1:1000); Anti-actin (MBL, PM053-7, 1:10,000). Uncropped blots in the Source Data file.