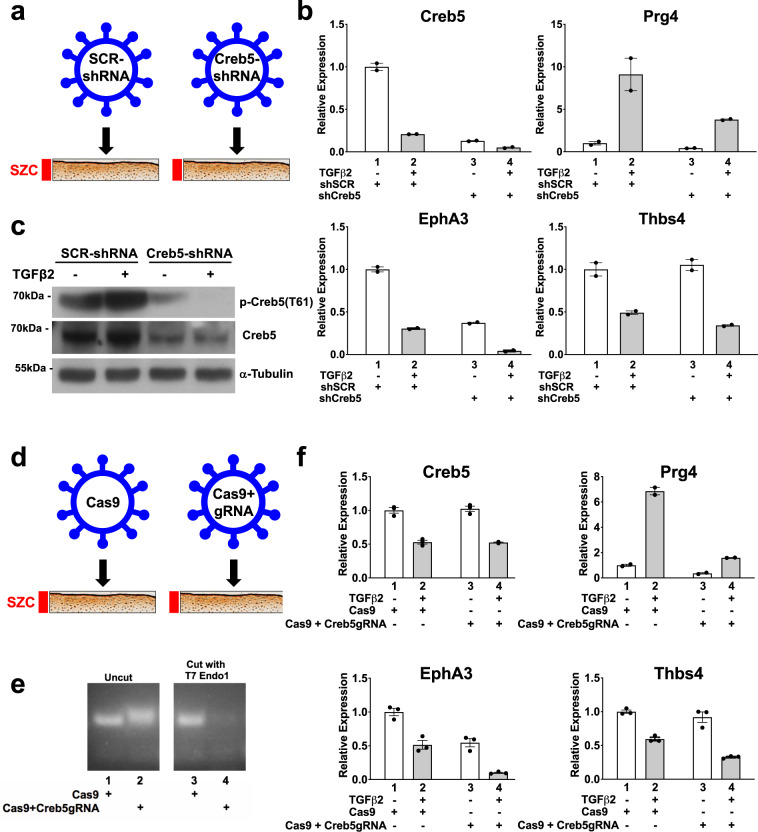
Fig. 3. Creb5 function is necessary for TGF-β-dependent induction of Prg4 in superficial zone articular chondrocytes.
a–c shRNA-mediated knock-down of Creb5 in superficial zone articular chondrocytes. SZCs were infected with a lentivirus encoding either control scrambled shRNA (shSCR, lanes 1 and 2) or shCreb5 (lanes 3 and 4), after selection in puromycin, the cells were cultured in either the absence (white) or presence (gray) of TGF-β2 (20 ng/ml) for 3 days. b Gene expression was assayed by RT-qPCR and normalized to Gapdh. Error bar indicates standard error of the mean (n = 2 technical repeats). Similar results have been obtained in three independent biological repeats. c Western analysis of proteins in SZCs recognized by antibodies directed against either phospho-Creb5 (T61), total Creb5, or α-tubulin. Similar results have been obtained in two independent biological repeats. d–f CRISPR-Cas9 mediated mutation of the DNA-binding domain of Creb5 in SZCs. SZCs were infected with a lentivirus encoding Cas9 alone or Cas9 plus a Creb5 guide RNA (targeting the DNA-binding domain), as indicated. After selection in puromycin, the cells were cultured in either the absence (white) or presence (gray) of TGF-β2 (20 ng/ml) for 3 days. e T7 Endonuclease 1 assay (which cleaves at mismatches) is displayed for the RT-PCR amplicon encoding the bZIP domain of Creb5. f Gene expression was assayed by RT-qPCR and normalized to Gapdh. Error bar indicates standard error of the mean (n = 3 technical repeats). Similar results have been obtained in two independent biological repeats.