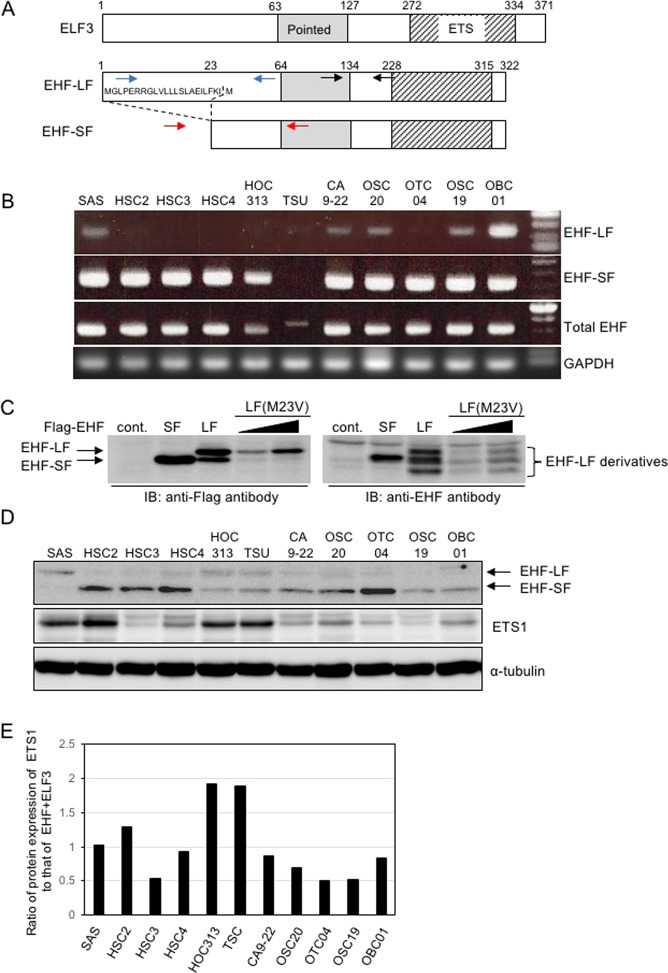
Fig. 2. Two variants of EHF.
A Schematic illustration of ELF3 and EHF gene products is shown. The long form variant of EHF includes 22 amino acid residues from exon 1 (EHF-LF), whereas the short form variant of EHF excludes exon 1 (EHF-SF). The pointed and ETS domains are shown as grey and hatched areas, respectively. The primers used to amplify EHF-LF, EHF-SF, and total EHF are shown in blue, red, and black arrows, respectively. B mRNA levels of two EHF transcript variants were analyzed by conventional RT-PCR. C and D IB with the indicated antibodies were performed in COS7 transfected with control vector (cont.) or the indicated plasmids (C), and in HNSCC cells (D). E ETS1 (D), EHF-SF (D), and ELF3 (S2B) protein levels were densitometrically quantified and compared with those of α-tubulin. The ratio of protein expression of ETS1/α-tubulin to that of EHF-SF/α-tubulin + ELF3/α-tubulin in SAS cells was indicated as “1”. α-tubulin was used as a loading control (D). EHF-LF(M23V), a mutant in which Met 23 in EHF-LF was substituted with Val (C).