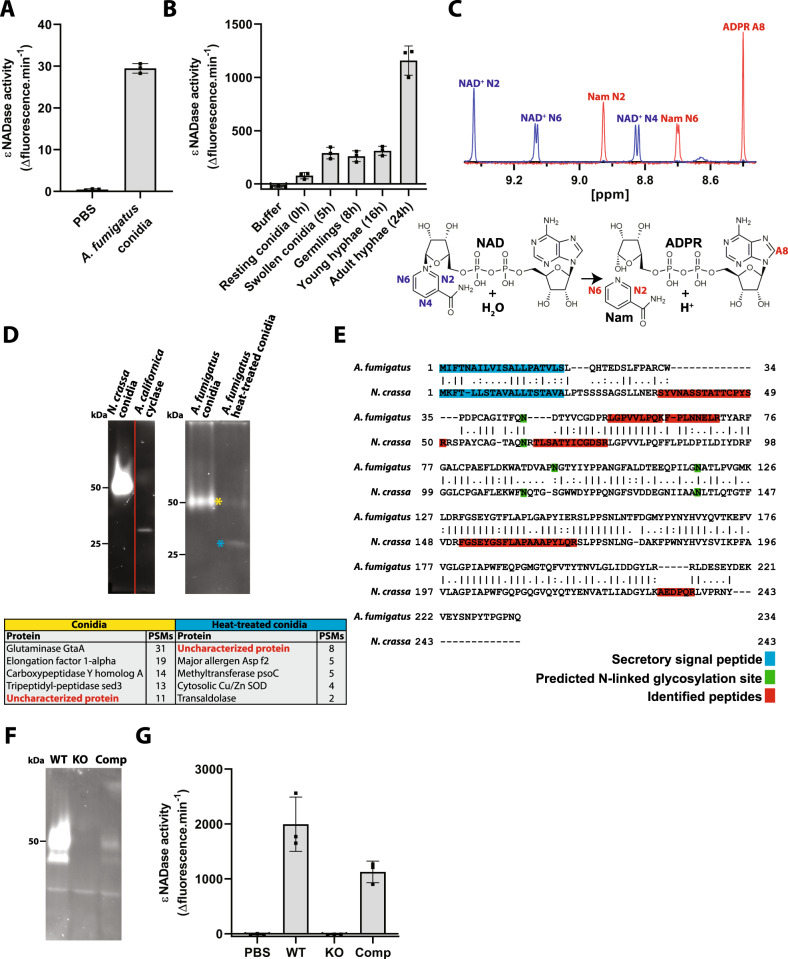
Fig. 1. Identification of fungal conidial NADases.
A NADase activity of A. fumigatus conidia demonstrated by a fluorometric assay using ɛNAD, n = 3. B NADase activity of different A. fumigatus growth stages demonstrated by a flurorometric assay using ɛNAD, n = 3. C Top: identification of nicotinamide (Nam) and ADP ribose (ADPR) as the NAD+ cleavage products following incubation with A. fumigatus conidia by 1H NMR. Bottom: Assignment of relevant NMR signals for NAD+ and its cleavage products. Hydrolysis of NAD+ leads to the formation of Nam and ADPR, the protons giving rise to the NMR signals are labelled blue for NAD+ and red for Nam and ADPR. D Identification of possible fungal NADases. Top: Enzyme activity gels of N. crassa and Aplysia californica cyclase, which was used as a positive control (left) and A. fumigatus (right) conidia developed with ɛNAD. In the right panel, the yellow and cyan asterisks denote the bands obtained with and without heat treatment, respectively. Fluorescent bands were excised and subjected to proteomics analysis. Bottom: Top hits of A. fumigatus proteins identified by mass spectrometry sorted by their peptide spectral matches score (PSM). The only overlapping hit between the two samples was an uncharacterized, predicted protein (highlighted in red). E Global pairwise alignment of predicted NADase sequences from A. fumigatus and N. crassa deduced from the genes identified based on the results shown in (D). The peptides that were detected in A. fumigatus and N. crassa conidia are highlighted in red. Bioinformatic analyses predict the presence of a secretory signal peptide and N-linked glycosylated asparagine residues, shown in blue and green, respectively. F In-gel ɛNADase assay of conidia from A. fumigatus wild type (WT), knockout mutant (KO) strain ΔnadA which lacks the gene predicted to encode the conidial NADase (AFUA_6G14470) and conidia from a complementation strain (Comp) ΔnadA:nadA. G Fluorometric assay of NADase activity of the samples described in (F), n = 3. Experiments in (A, B, D, F, G) were performed independently three times with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.