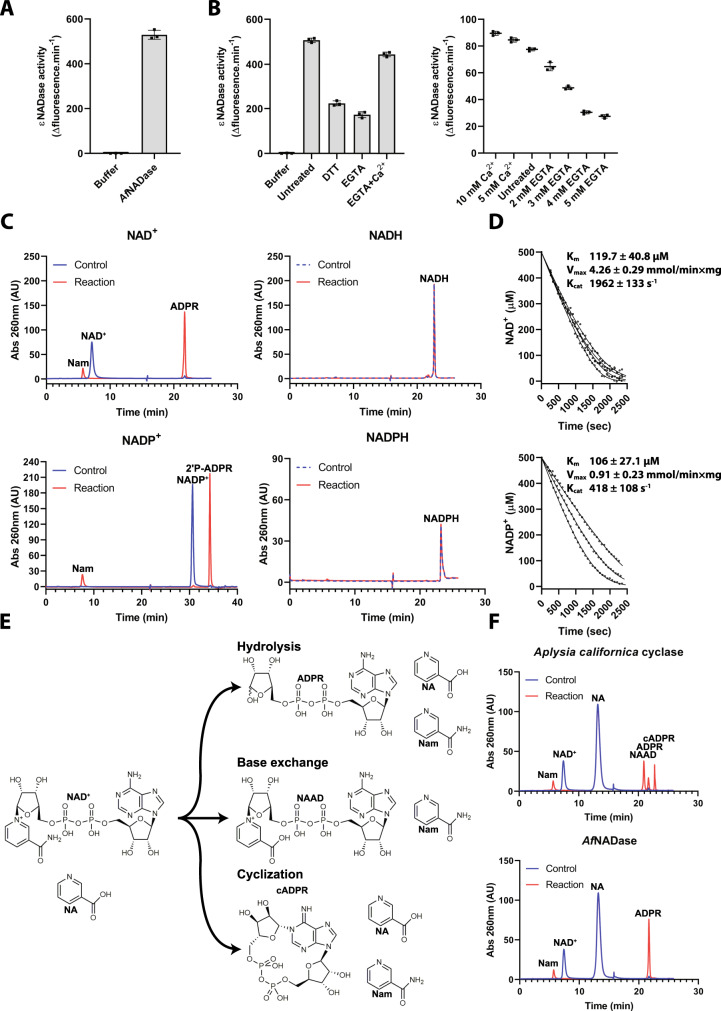
Fig. 2. AfNADase is a pure NAD(P)+ glycohydrolase.
A NADase activity of recombinant AfNADase purified from Sf9 insect cells measured by the fluorescence assay using ɛNAD, n = 3. B left: NADase activity of recombinant AfNADase from Sf9 insect cells treated with DTT, EGTA or EGTA and calcium chloride, n = 3 Right: NADase activity of AfNADase from Sf9 insect cells titrated with EGTA and CaCl2. C identification of AfNADase substrate specificity by HPLC. The HPLC chromatograms display AfNADase mediated reactions using the indicated substrates. D Kinetics of NAD+ and NADP+ hydrolysis by AfNADase determined by 1H NMR. The integral of the resonances corresponding to NAD+ N-2 and N-6 were plotted and used for curve fitting. E Absence of ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity in AfNADase. In the presence of an excess of NA some NADases (namely ADP-ribosyl cyclases) can catalyse the exchange of the Nam moiety in NAD+ for NA producing NAAD (“base-exchange reaction”). Cyclases can also produce cyclic ADPR or simply cleave NAD+ to ADPR and Nam. F AfNADase does not possess base-exchange or ADPR cyclase activity, identifying it as pure NADase. HPLC chromatograms of AfNADase and Aplysia californica cyclase base exchange reactions. Experiments in (A, B, C, F) were performed independently three times with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.