Figure 2. Coxsackievirus B (CVB) 3 infection of pregnant dams leads to fetal cardiac defects and death.
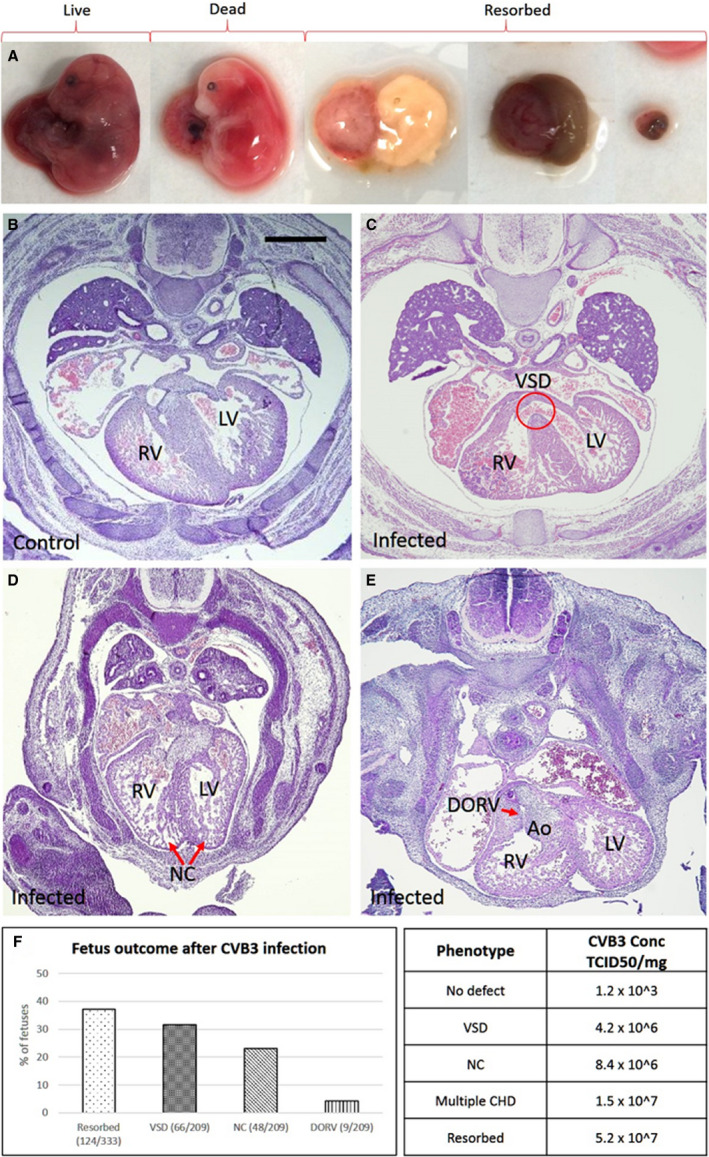
A, Representative images of embryonic day (E) 17 fetuses from CVB3‐infected dams, exhibiting specific phenotypes (left to right): viable, fully formed dead, and 3 images showing fetuses at various stages of resorption. B–E, Hematoxylin and eosin–stained heart sections of E17 fetuses from uninfected (B) and infected dams (C–E), and the various cardiac defects are indicated. F, Graph showing the percentage of fetuses from CVB3‐infected dams with the indicated cardiac defects. The χ2 test was used to analyze statistical significance between control and test groups by calculating P values. Table showing the amount of virus present in resorbed fetuses and fetuses with congenital heart defect (CHD), determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction using CVB3 quantification standard curve (Figure 1d). Part of resorbed fetus and lower torso of fully formed fetuses were used to assess viral load. Bar=100 µm. Ao indicates aorta; DORV, double‐outflow RV; LV, left ventricle; NC, noncompaction; RV, right ventricle; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infective dose; and VSD, ventricular septum defect.
