Figure 5. DUSP26 inhibited TAK1‐p38/JNK signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.
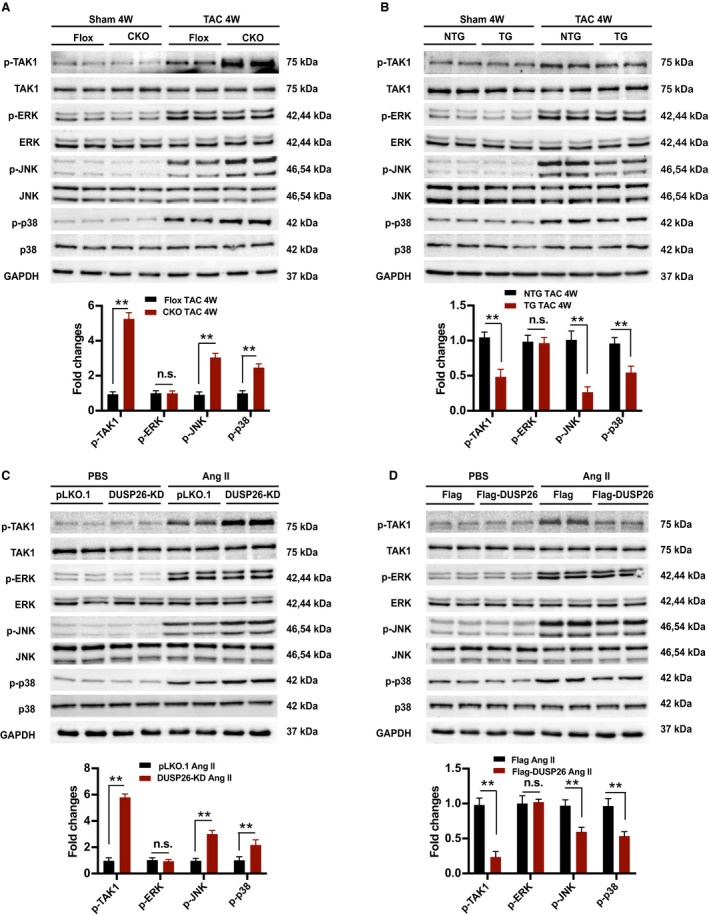
A, Western blot and quantification results of the phosphorylation and total protein levels of TAK1, ERK, JNK, and p38 in the hearts of Flox and DUSP26‐CKO mice 4 weeks after sham or TAC operation (n=4 per group). B, Western blot and quantification results of the phosphorylation and total protein levels of TAK1, ERK, JNK, and p38 in the hearts of DUSP26‐TG and nontransgenic mice 4 weeks after sham or TAC operation (n=4 per group). C, H9C2 cells were infected with lentiviruses targeting DUSP26 or nontargeting pLKO.1 vector and treated with angiotensin II (1 μmol/L) or PBS for 48 hours. D, Western blot measurement and quantification results of phosphorylation and total protein levels of TAK1, ERK, JNK, and p38 in H9C2 cells infected with Flag‐DUSP26 or Flag‐control and treated with angiotensin II (1 μmol/L) or PBS for 48 hours. Data are presented as the mean±SD. **P<0.01. CKO indicates conditional knockout; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; JNK, c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; n.s., no significance between the 2 indicated groups; p38, p38 kinase; TAC, transverse aortic constriction; and TAK1, transforming growth factor‐β activated kinase 1.
