Figure 3. Right ventricle (RV) failure is characterized by increased oxidative stress.
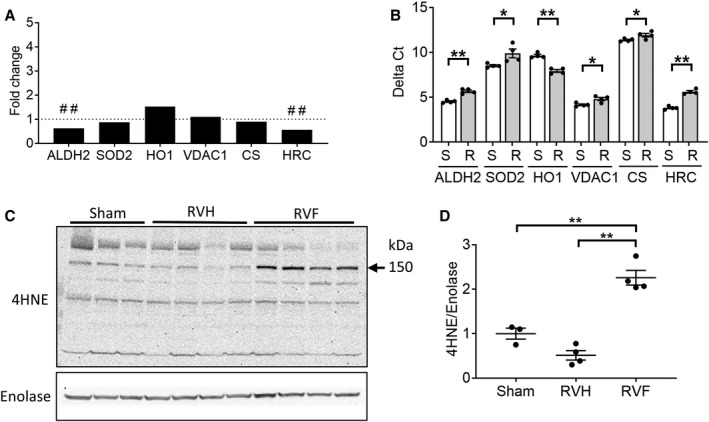
A, RV failure compared with sham‐operated RV controls demonstrated deceased expression in antioxidant defense genes (aldehyde dehydrogenase 2, superoxide dismustase 2), increased expression of the oxidative stress marker, heme oxygenase 1, decreased expression of the repressor of mitochondrial apoptosis (HRC [histidine rich calcium binding protein]) while the expression of mitochondrial housekeeping genes (voltage‐dependent anion channel, citrate synthase) were unchanged (n=4/group). B, The same genes were validated by real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and demonstrated decreased expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2, superoxide dismutase 2, and HRC and increased expression of heme oxygenase 1 in RV failure compared with sham‐operated RV controls using t‐test (n=4/group). Raw data are shown as Delta Ct=Ct (target gene)−Ct (β‐actin housekeeping gene). A decrease in delta Ct denotes an increase in expression. C and D, Protein expression of 4HNE (4‐hydroxynonenal), a marker of oxidative stress, was increased in RV failure using one‐way ANOVA, (n=3–4/group). Data are presented as mean±SEM. 4HNE indicates 4‐hydroxynonenal; ALDH2, aldehyde dehydrogenase 2; CS, citrate synthase; HO1, heme oxygenase 1; HRC, histidine rich calcium binding protein; RV, right ventricle; RVF, RV failure; RVH, RV hypertrophy; SOD2, superoxide dismutase 2; and VDAC1, voltage‐dependent anion‐selective channel protein 1. ##q<0.01, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
