Figure 2.
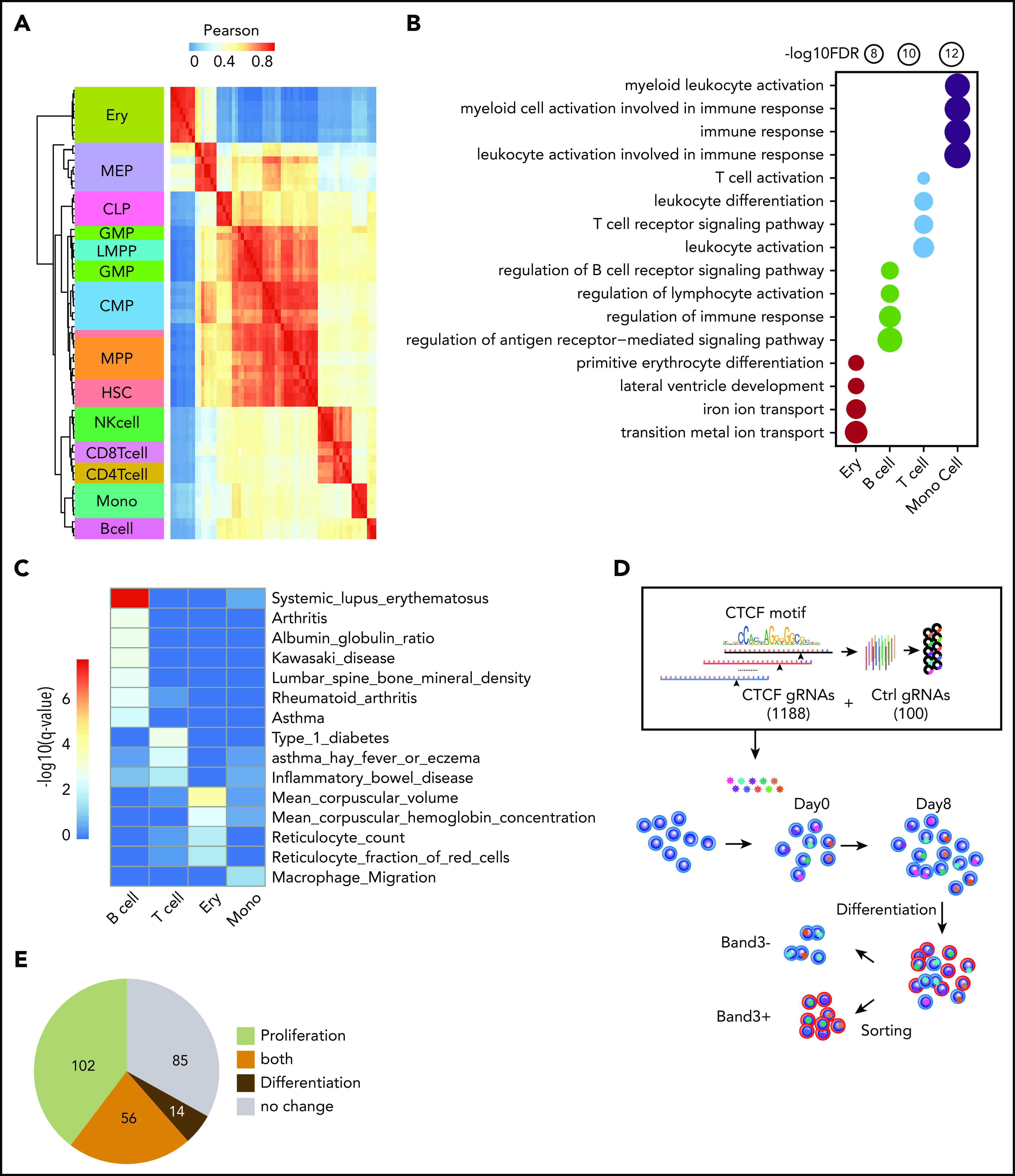
Functional importance of dynamic CTCF-binding sites. (A) Heatmap showing the unsupervised hierarchical clustering based on Pearson correlation of ATAC-seq signals on dynamic CTCF peaks across different blood lineages. The hierarchical cluster was generated based on the Pearson correlation of normalized ATAC-seq signals within dynamic CTCF sites. The chromatin accessibility within dynamic CTCF sites in each blood cell types were calculated based on ATAC-seq data generated in the previous publication.19 (B) Functional annotation results of dynamic CTCF sites for the top Gene Ontology cellular component and phenotype from GREAT. The radius of the circle represents the significance, −log10(FDR), of the enrichment. (C) Enrichment significance of trait-associated SNPs within different types of dynamic CTCF-binding sites. (D) Schematic of the pooled sgRNA library design and screening procedure used to experimentally validate the function of dynamic CTCF-binding sites. (E) Pie chart showing the numbers of dynamic CTCF-binding sites with different functions based on sgRNA perturbation results. CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; CMP, common myeloid progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-monocyte progenitor; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; LMPP, lymphomyeloid primed progenitor; MEP, megakaryocytic-erythroid progenitor; MPP, myeloid primed progenitor; NK, natural killer.
