Figure 3. ExoCDNF protects isolated hearts from injuries provoked by I/R and the protection is prevented by wortmannin, a PI3K/AKT antagonist.
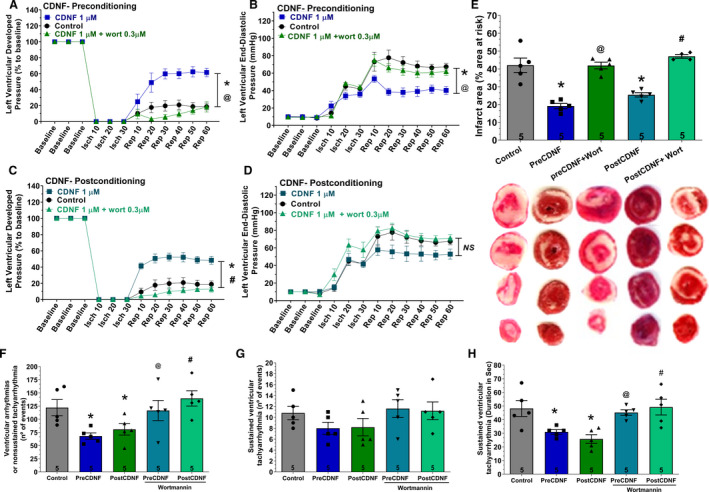
Time courses of left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP) (A and C) and left ventricular end‐diastolic pressure (LVEDP) (B and D) during I/R protocol. In A and B, CDNF (1 µmol/L) was perfused 5 minutes before ischemia (preconditioning) and in C and D, during the first 5 minutes of reperfusion (postconditioning). Wortmannin (0.3 µmol/L) was perfused 5 minutes before CDNF. E, Infarct area of hearts. Representative cross‐section images of TCC‐stained ventricle hearts subjected to I/R. F, The number of ventricular arrhythmias or nonsustained tachyarrhythmia events. G, The number of events and (H) the duration of sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmia produced during reperfusion. Values are expressed as means±SEM. Number in each column is n of hearts. NS, not significant; *P<0.01 vs control; @ P<0.01 vs preCDNF and # P<0.01 vs postCDNF with 1‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests for infarct area and arrhythmias analysis and 2‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests for LVDP and LVEDP analysis. AKT indicates protein kinase B; CDNF, cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; and TCC, triphenyltetrazolium chloride.
