Figure 4. ExoCDNF treatment increases the level of phosphorylated AKT (p‐AKT) in rat isolated hearts and in mouse and human cardiomyocytes.
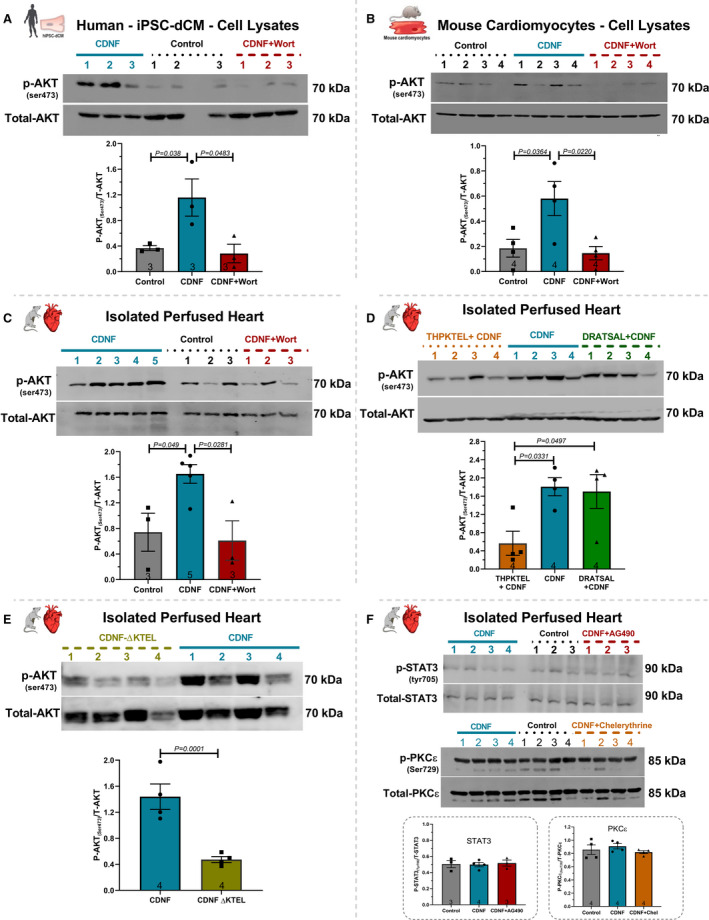
Cultures of (A) hiPSC‐dCM or (B) mouse cardiac myocytes were treated with CDNF (1 µmol/L/20 hours) or with wortmannin (0.3 µmol/L/15 minutes) before CDNF addition. In (C), rat isolated hearts were perfused with CDNF (1 µmol/L/5 minutes, preconditioning) before I/R either alone or in combination with wortmannin (0.3 µmol/L/5 minutes) before CDNF treatment. D, The peptide THPKTEL that binds to the KDEL‐R blocks CDNF‐induced PI3K/AKT activation. Isolated hearts were perfused with CDNF (1 µmol/L/5 minutes, preconditioning) before I/R either alone or in combination with THPKTEL or with the scrambled peptide DRATSAL (peptides added 5 minutes before CDNF treatment and during the 5 minutes CDNF treatment). E, CDNF‐ΔKTEL was unable to activate p‐AKT in isolated perfused hearts. Isolated hearts were perfused with CDNF‐ΔKTEL (1 µmol/L/5 minutes) before I/R. The intensities of the p‐AKT bands were normalized to total‐AKT levels. F, The STAT3 inhibitor (AG490, 10 µmol/L/5 minutes) and the PKC inhibitor (chelerythrine, 10 µmol/L/5 minutes) not abolished the protection generated by CDNF. Isolated hearts were perfused with CDNF (1 µmol/L/5 minutes, preconditioning) before I/R either alone or in combination with AG490, 10 µmol/L/5 minutes or chelerythrine, 10 µmol/L/5 minutes before CDNF treatment. The number of experiments is equal to the number of lanes. The data were expressed as means±SEM, with 1‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc tests. AKT indicates protein kinase B; CDNF, cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor; and iPSC‐dCM, iPSC‐dCM, induced pluripotent stem cells differentiated into cardiomyocytes.
