Figure 9. Schematic representation of the main findings of the present study.
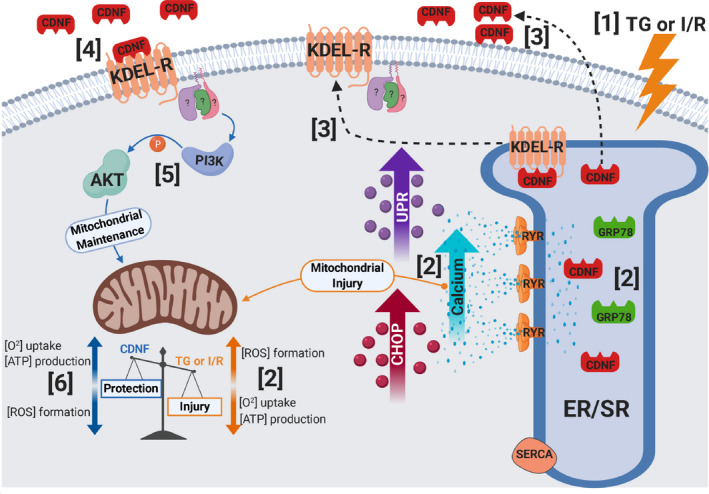
(1) TG or I/R induce cellular injuries causing (2) an increase in cytosolic calcium and UPR activation, upregulation of GRP78, CDNF, and CHOP, as well as mitochondria impairment (decrease in [O2] and [ATP] and an increase in [ROS]). (3) CDNF is an ER/SR‐resident protein remaining bound to KDEL‐R through its degenerated KTEL sequence located at the C‐terminal end. Under stress, KDEL‐R and CDNF dissociate and migrate from the ER/SR to the cell membrane and extracellular milieu, respectively, (4) allowing the binding of CDNF to the KDEL‐R at the cell surface with the subsequent (5) activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway either directly or indirectly conferring (6) mitochondrial maintenance and cell survival (cardioprotection). CDNF indicates cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor; CHOP, CCAAT/‐enhancer‐binding protein homologous protein; ER/SR, endoplasmic reticulum/sarcoplasmic reticulum; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RYR, ryanodine receptor; SERCA, sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+‐ATPase; TG, thapsigargin; and UPR, unfolding protein response.
